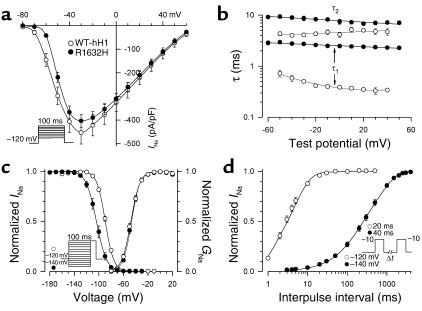
Figure 7.
Biophysical properties of R1632H. (a) Comparison of current-voltage relationship for WT-hH1 (open circles) and R1632H (filled circles, n = 25). Current is normalized to cell capacitance to give a measure of sodium current density. There is no difference in current density between WT-hH1 and R1632H at all tested voltages. (b) Voltage dependence of fast inactivation time constants for WT-hH1 (open circles) and R1632H (filled circles, n = 25). Differences between WT-hH1 and mutant channel were significant for τ1 (P < 0.0001) and τ2 (P < 0.05) at voltages between –60 to +50 mV. (c) Voltage dependence of sodium channel availability and activation (symbol definitions are shown as an inset, and their shading patterns are explained in the y-axis labels). Voltage dependence of sodium channel availability (steady-state inactivation) was obtained using a two-pulse protocol as illustrated by the inset. The membrane potentials for half-maximal inactivation and slope factors are provided in Table 2. The activation curve was constructed as described in the legend of Figure 5, and parameters are given in Table 2. (d) Time course of recovery from inactivation at –120mV (–140 mV for R1632H). The time constants and fractional amplitudes (given in parentheses) are provided in Table 2.