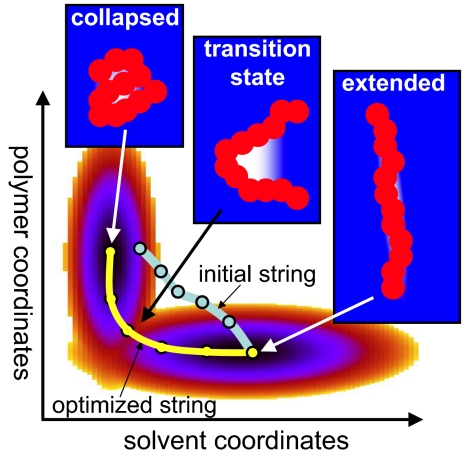
Fig. 1.
Schematic free-energy surface of hydrophobic polymer collapse as a function of polymer and solvent degrees of freedom. At the transition state, water (blue) recedes from a kink near the middle of the polymer (red), forming a small “vapor bubble” (white). In the string method (6, 14), an initial guess for the reaction path (light blue), consisting of a sequence of configurations (circles), is iteratively optimized to find the string representing the dominant reaction path (yellow).