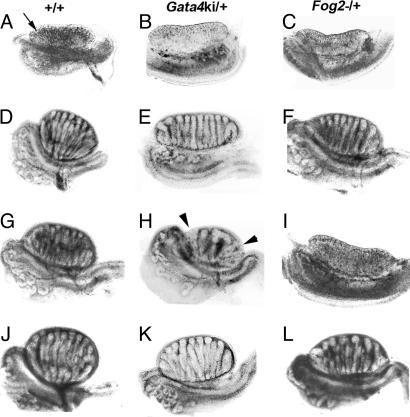
Fig. 1.
Embryonic day (E) 14.5–15 gonad–mesonephros complexes from normal (+/+) (A, D, G, and J), and heterozygous mutant Gata4ki (Gata4ki/+) (B, E, H, and K), and Fog2− (Fog2−/+) (C, F, I, and L) fetuses. (A) B6+/+ XX ovary. (B) B6 Gata4ki/+ XX ovary. (C) B6 Fog2−/+ XX ovary. (D) B6+/+ XYB6 testis. (E) B6 Gata4ki/+ XYB6 testis. (F) B6 Fog2−/+ XYB6 testis. (G) B6+/+ XYAKR testis. (H) B6 Gata4ki/+ XYAKR ovotestis. (I) B6 Fog2−/+ XYAKR ovary. (J) (B6 × D2)F1+/+ XYAKR testis. (K) (B6 × D2)F1 Gata4ki/+ XYAKR testis. (L) (B6 × D2)F1 Fog2−/+ XYAKR testis. In each case, the gonad (arrow in A) lies above the mesonephros. (E) Testis with attenuated cord growth. (H) Ovotestis. The arrowheads in H point to ovarian tissue.