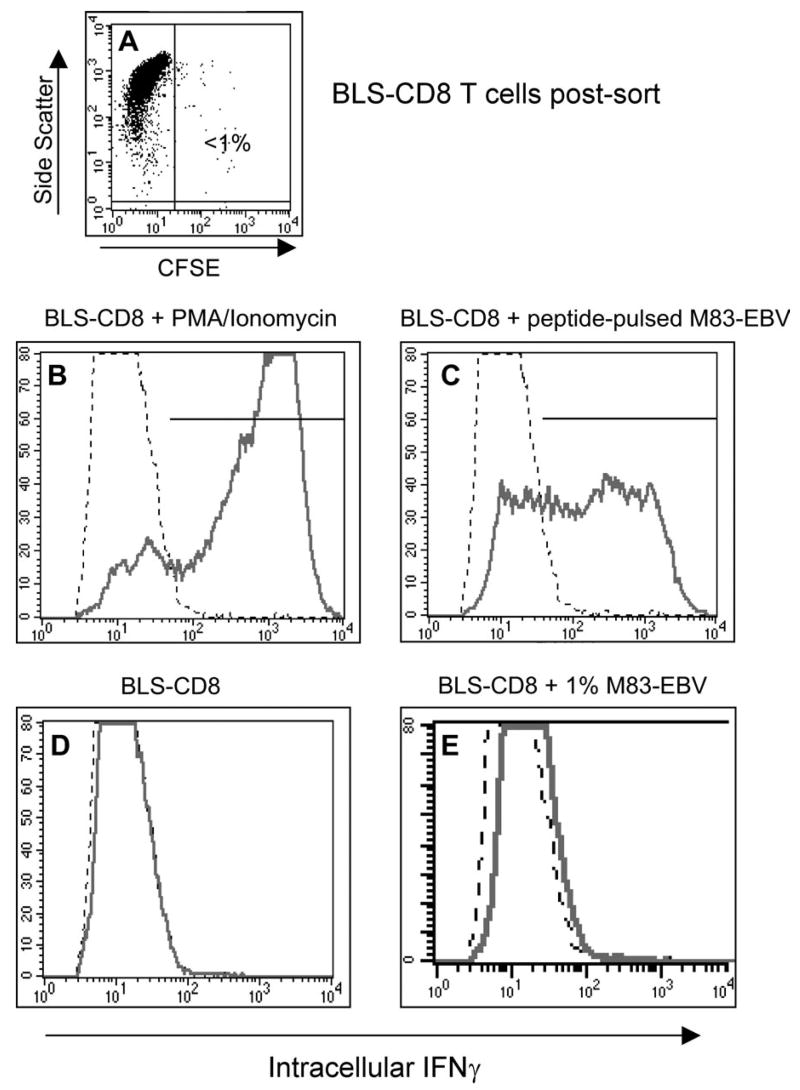
Fig. 9.
T cells with acquired MHC class II can function as APC for helper T cells. BLS-CD8 T cells were incubated with CFSE labeled, peptide-pulsed (10 μg/ml EBNA2280–290 peptide for 4 h) M83-EBV cells (HLA-DQ2+) at a 1:1 ratio overnight. Next day, the CFSE negative T cells were purified by flow sorting (>98% purity, panel A) and were co-incubated with antigen specific HLA-DQ2 restricted M14-HTL at 1:1 ratio for 5 h. Antigen response of the M14-HTL was measured by intracellular staining for IFNγ. The percentage of IFNγ positive M14-HTL was detected by flow cytometric analysis by gating on the CD4+ Tcell population. As a positive control, M14-HTL were activated by 50 ng/ml PMA plus 1 μg/ml calcium ionophore (B). IFNγ expression by M14-HTL (gated on CD4+ cells) incubated with BLS-CD8 cells that acquired MHC class II (C). IFNγ expression of M14-HTL incubated with control BLS-CD8 T cells, without M83-EBV pre-incubation (D). Since the contamination of the flow sorted BLS-CD8 Tcells was ~1% (A), as an additional control BLS-CD8 Tcells were mixed with 1% peptide pulsed M83-EBV cells and incubated with M14-HTL (E), demonstrating that this level of contamination was not sufficient to activate the M14-HTL. This experiment was repeated twice with similar results.