Figure 3.
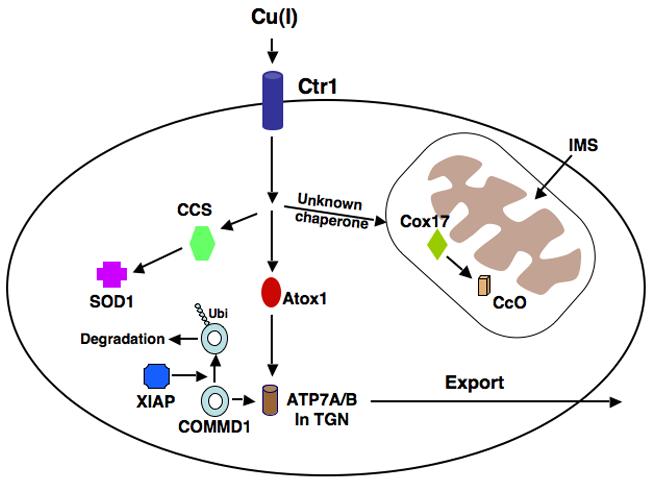
Model of copper uptake and metabolism. Copper enters the cell via the high affinity copper transporter, Ctr1. Atox1 is the chaperone responsible for transporting copper to the P-type ATPases 7A and 7B in the trans Golgi network (TGN). The chaperone, CCS, delivers Cu to cytosolic Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase (SOD1), and Cox17, in the mitochondria, delivers Cu to Cytochrome c Oxidase (CcO). The manner in which copper is transported from the cytosol to Cox 17 in the mitochondria has not been fully elucidated. COMMD1 promotes the efflux of copper from the cell, probably via its interaction with ATP7B. XIAP may reduce copper export by acting as an E3 Ubiquitin ligase and promoting the degradation of COMMD1.
