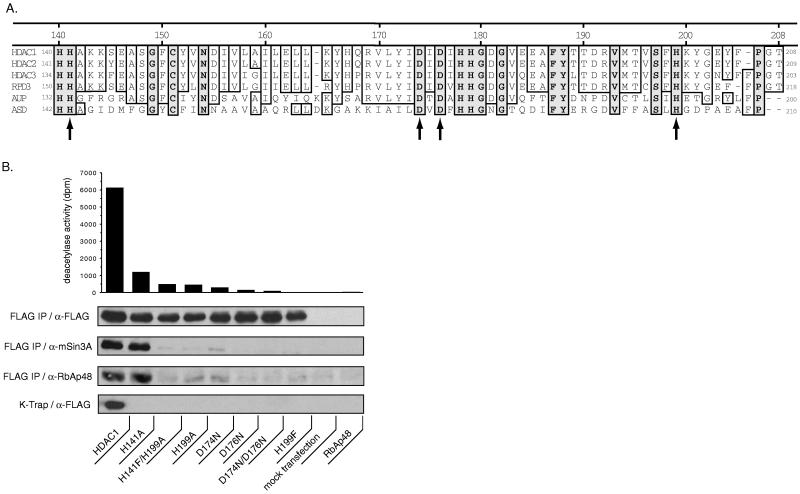
Figure 4.
Mutagenesis of HDAC1 identifies important catalytic and/or structural residues in the enzyme. (A) Amino acid sequence alignment of a conserved region of HDAC1 with other eukaryotic HDACs, and with the related prokaryotic acetoin utilization protein (AUP) and acetyl polyamino amidohydrolase (ASD). Completely conserved residues are boxed in gray. Residues targeted for mutation in this study are indicated by an arrow. Other residues with potential roles in catalysis include His-140, Cys-151, His-178, His-179, Tyr-188, and Ser-197. (B) HDAC1 mutant analysis: All wild-type and mutant constructs contained C-terminal FLAG-epitope tags used to immunoprecipitate (FLAG IP) the overexpressed proteins from transfected SV40 T-Ag Jurkat cells. FLAG IPs were tested for deacetylase activity and immunoblotted by using the antibodies indicated to determine immunoprecipitation efficiency (α-FLAG) and coprecipitated proteins (α-mSin3A and α-RbAp48). A background of 444 dpm from the mock transfection (no DNA) IP was subtracted from each IP to normalize deacetylase activity. Extracts from a separate transfection were incubated with K-trap matrix and immunoblotted with α-FLAG antibody. RbAp48 (in pBJ5) is an additional negative control.