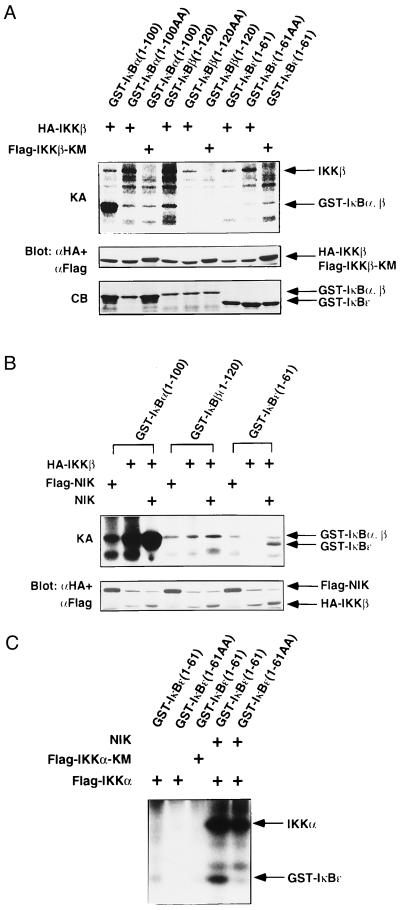
Figure 3.
In vitro phosphorylation of IκBα, -β, and -ɛ by IKKβ and IKKα. (A) Specificity of IκBs phosphorylation by IKKβ. 293 cells were transiently transfected with expression vector for HA-IKKβ or Flag-IKKβ-KM. Twenty-four hours after transfection, IKKβ proteins were immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag or anti-HA mAb. The precipitates were incubated with GST-IκBα(1–100), GST-IκBα(1–100) (S32A, S36A; designated as 1–100AA), GST-IκBβ(1–120), GST-IκBβ(1–120) (S29A, S32A; designated as 1–120AA), GST-IκBɛ(1–61), or GST-IκBɛ(1–61) (S18A, S22A; designated as 1–61AA) and [γ-32P]ATP, resolved by SDS/PAGE, and analyzed by autoradiography. The kinase activity (KA) is indicated (Top). The amounts of IKKβ and IKKβ-KM were determined by immunoblotting with anti-Flag and anti-HA mAbs (Middle). The amounts of GST-fusion proteins were assessed by Coomassie Blue (CB) staining (Bottom). Right arrows mark the positions of each protein. (B) NIK enhances phosphorylation of IκBs by IKKβ. 293 cells were transiently transfected with expression vectors for HA-IKKβ, Flag-NIK, and/or NIK. HA-IKKβ or Flag-NIK was immunoprecipitated and incubated with GST-IκBα(1–100), GST-IκBβ(1–120), or GST-IκBɛ(1–61) in the presence of [γ-32P]ATP. The kinase activity (KA) is indicated (Upper). The amounts of HA-IKKβ and Flag-NIK were determined by immunoblotting with anti-Flag and anti-HA mAbs (Lower). The positions of each protein are indicated at the right. (C) NIK enhances phosphorylation of IκBɛ by IKKα. 293 cells were transiently transfected with expression vectors for FlagIKKα, Flag-IKKα-KM, and/or NIK. Flag-tagged proteins were immunoprecipitated, and in vitro phosphorylation of GST-IκBɛ(1–61) or GST-IκBɛ(1–61AA) was performed as in A. The positions of phosphorylated IKKα and GST-IκBɛ are indicated (Right).