Abstract
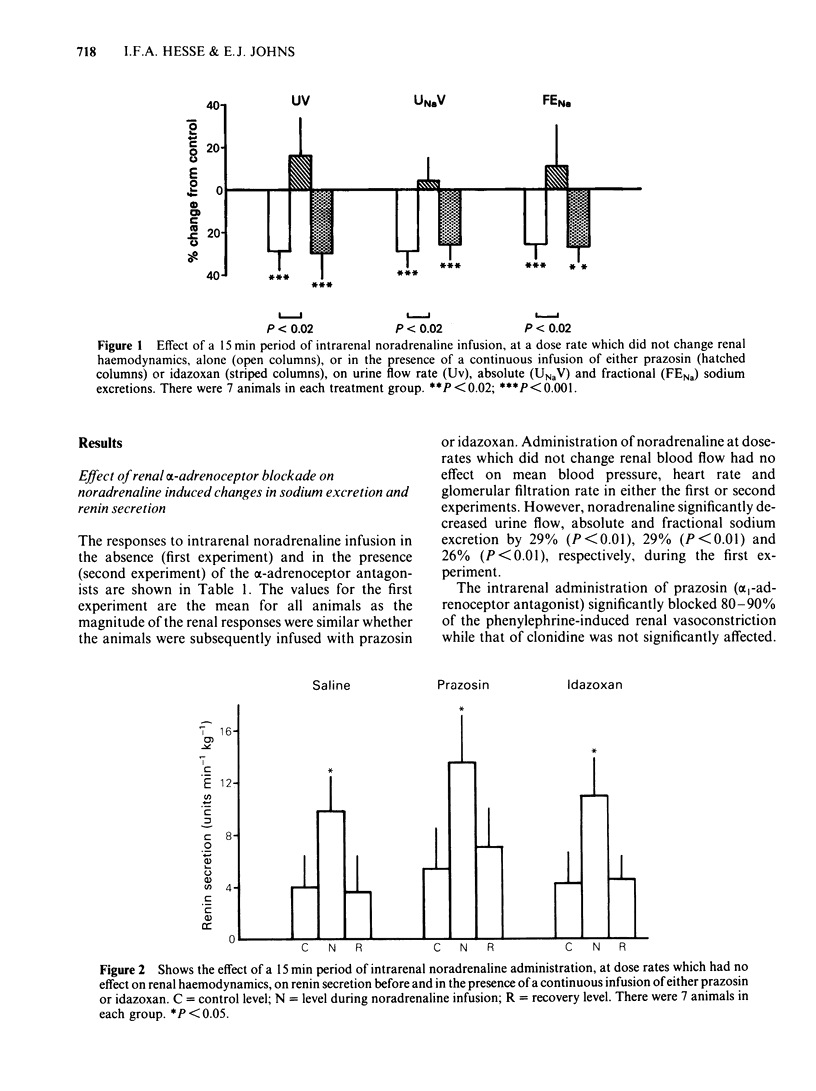
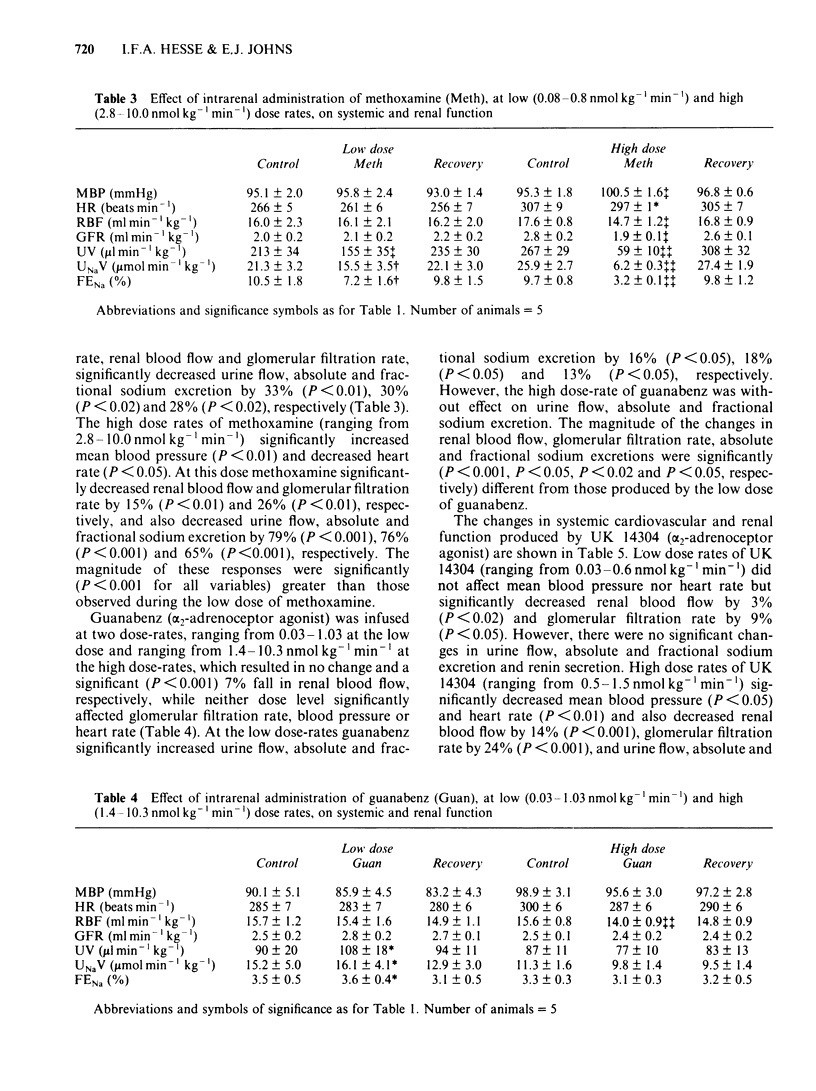
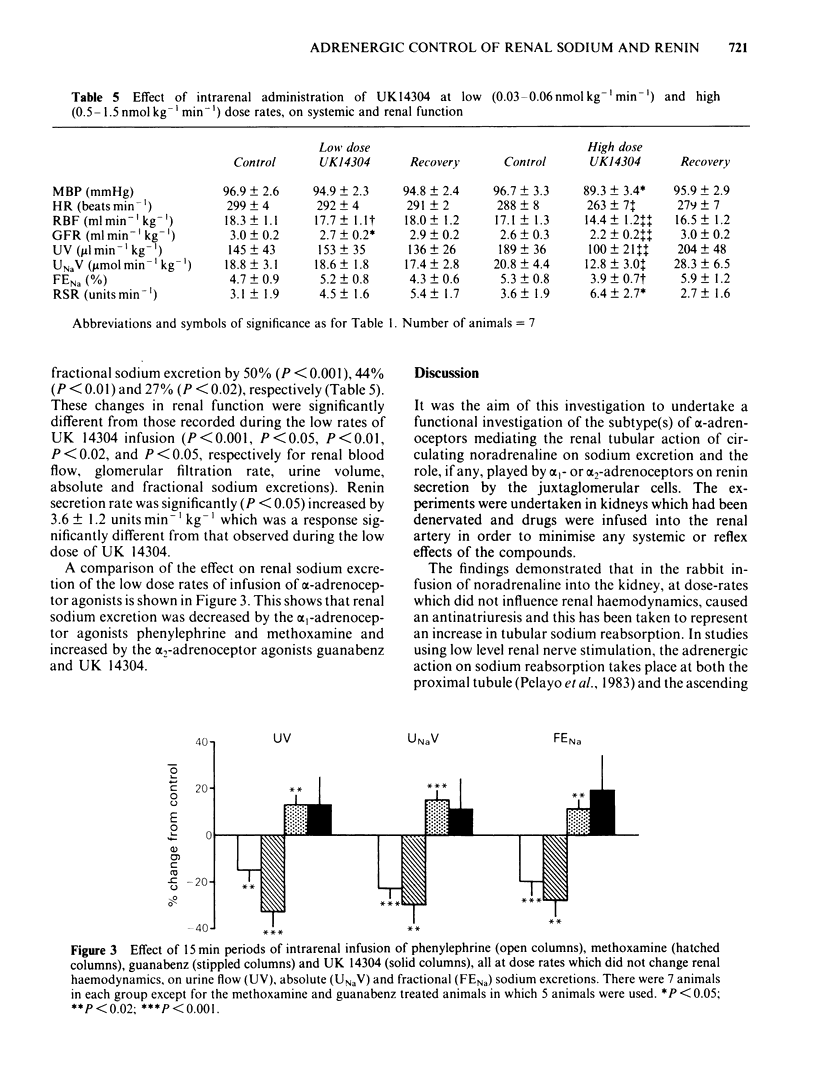
A study was undertaken in the anaesthetized rabbit to classify the alpha-adrenoceptor subtypes responsible for increasing renal tubular sodium reabsorption and renin secretion. Intrarenal administration of noradrenaline, at doses which did not change renal blood flow or glomerular filtration rate, significantly decreased urine flow, absolute and fractional sodium excretion by between 26% and 29%. These renal responses to noradrenaline were abolished by the selective alpha 1-adrenoceptor antagonist, prazosin, but not by the selective alpha 2-adrenoceptor antagonist, idazoxan. Noradrenaline, given intrarenally, increased renin secretion between two and three fold and this response was not modified by either prazosin or idazoxan. Intrarenal administration of the selective alpha-adrenoceptor agonists, phenylephrine and methoxamine, at dose rates which did not change renal haemodynamics, significantly reduced urine flow, absolute and fractional sodium excretion by 15% to 33%, but at doses which reduced blood flow and filtration rate, by between 11% and 26%, urine flow, absolute and fractional sodium excretion decreased between 42% and 49%. Infusion of guanabenz (selective alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonist), at doses with no renal haemodynamic action, increased urine flow, absolute and fractional sodium excretion by 11% to 15%, while at doses which decreased blood flow by 7%, these other variables did not change. Administration of UK 14304 (selective alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonist) reduced blood flow and filtration rate by 3% and 9% respectively but had no other measurable action. At higher doses, which decreased blood flow by 14% and filtration rate by 24%, urine flow, absolute and fractional sodium excretion fell by between 27% and 50%. Renin secretion was significantly increased by the high doses of phenylephrine and UK 14304 but not by the low doses of these drugs. These studies show that adrenergic stimulation of renal tubular sodium reabsorption involves the activation of alpha 1- but not alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Further, adrenergic activation of the juxtaglomerular cells to release renin does not appear to involve either alpha 1- or alpha 2-adrenoceptors.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARGER A. C., MULDOWNEY F. P., LIEBOWITZ M. R. Role of the kidney in the pathogenesis of congestive heart failure. Circulation. 1959 Aug;20(2):273–285. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.20.2.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOJESEN E. A method for determination of inulin in plasma and urine. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1952;266:275–282. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1952.tb13376.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell-Reuss E., Trevino D. L., Gottschalk C. W. Effect of renal sympathetic nerve stimulation on proximal water and sodium reabsorption. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):1104–1107. doi: 10.1172/JCI108355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair M. L. Stimulation of renin secretion by alpha-adrenoceptor agonists. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jan;244(1):E37–E44. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1983.244.1.E37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambridge D., Davey M. J., Massingham R. Prazosin, a selective antagonist of post-synaptic alpha-adrenoceptors [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Mar;59(3):514P–515P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambridge D. UK-14,304, a potent and selective alpha2-agonist for the characterisation of alpha-adrenoceptor subtypes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jul 10;72(4):413–415. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90588-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capponi A. M., Vallotton M. B. Renin release by rat kidney slices incubated in vitro. Role of sodium and of alpha- and beta-adrenergic receptors, and effect of vincristine. Circ Res. 1976 Aug;39(2):200–203. doi: 10.1161/01.res.39.2.200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desaulles E., Forler C., Velly J., Schwartz J. Effect of catecholamines on renin release in vitro. Biomedicine. 1975 Sep;22(5):433–439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiBona G. F., Sawin L. L. Effect of renal nerve stimulation on NaCl and H2O transport in Henle's loop of the rat. Am J Physiol. 1982 Dec;243(6):F576–F580. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.243.6.F576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doxey J. C., Roach A. G., Smith C. F. Studies on RX 781094: a selective, potent and specific antagonist of alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Mar;78(3):489–505. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb08809.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doxey J. C., Smith C. F., Walker J. M. Selectivity of blocking agents for pre-and postsynaptic alpha-adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 May;60(1):91–96. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb16752.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill J. R., Jr, Casper A. G. Effect of renal alpha-adrenergic stimulation on proximal tubular sodium reabsorption. Am J Physiol. 1972 Nov;223(5):1201–1205. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.223.5.1201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesse I. F., Johns E. J. The subtype of alpha-adrenoceptor involved in the neural control of renal tubular sodium reabsorption in the rabbit. J Physiol. 1984 Jul;352:527–538. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns E. J. An investigation into the type of beta-adrenoceptor mediating sympathetically activated renin release in the cat. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Jul;73(3):749–754. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb16811.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keeton T. K., Campbell W. B. The pharmacologic alteration of renin release. Pharmacol Rev. 1980 Jun;32(2):81–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobinger Central alpha-adrenergic systems as targets for hypotensive drugs. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1978;81:39–100. doi: 10.1007/BFb0034091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopp U., Aurell M., Sjölander M., Ablad B. The role of prostaglandins in the alpha- and beta-adrenoceptor mediated renin release response to graded renal nerve stimulation. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Jul;391(1):1–8. doi: 10.1007/BF00580685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. C. Evidence for more than one type of post-junctional alpha-adrenoceptor. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Feb 15;31(4):467–484. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson G. A., Summers R. J. A study of alpha 1-adrenoceptors in rat renal cortex: comparison of [3H]-prazosin binding with the alpha 1-adrenoceptor modulating gluconeogenesis under physiological conditions. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Sep;77(1):177–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb09284.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson G. A., Summers R. J. Localisation of [3H]clonidine binding to membranes from guinea pig renal tubules. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Feb 15;31(4):583–587. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90163-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson G. A., Summers R. J. [3H]prazosin and [3H]clonidine binding to alpha-adrenoceptors in membranes prepared from regions of rat kidney. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1981 Mar;33(3):189–191. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1981.tb13752.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson R. D., Nies A. S., Gerber J. G. Catecholamine-induced renin release in the anesthetized mongrel dog is due to both alpha and beta adrenoceptor stimulation: evidence that only the alpha adrenoceptor component is prostaglandin mediated. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Mar;224(3):483–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn J. L., DiBona G. F., Thames M. D. Beta-1 receptor mediation of renin secretion elicited by low-frequency renal nerve stimulation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Feb;216(2):265–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn J. L., DiBona G. F., Thames M. D. Role of renal alpha-adrenoceptors mediating renin secretion. Am J Physiol. 1982 Jun;242(6):F620–F626. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.242.6.F620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn J. L., Holdaas H., Thames M. D., DiBona G. F. Renal adrenoceptor mediation of antinatriuretic and renin secretion responses to low frequency renal nerve stimulation in the dog. Circ Res. 1983 Sep;53(3):298–305. doi: 10.1161/01.res.53.3.298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson J. E., Williams R. L. Analysis of direct renal actions of alpha and beta adrenergic stimulation upon sodium excretion compared to acetylcholine. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1968 Jun;33(2):223–241. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb00984.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelayo J. C., Ziegler M. G., Jose P. A., Blantz R. C. Renal denervation in the rat: analysis of glomerular and proximal tubular function. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jan;244(1):F70–F77. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.244.1.F70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettinger W. A., Keeton T. K., Campbell W. B., Harper D. C. Evidence for a renal alpha-adrenergic receptor inhibiting renin release. Circ Res. 1976 May;38(5):338–346. doi: 10.1161/01.res.38.5.338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K., Endo T., Taube H. D. Relative pre- and postsynaptic potencies of alpha-adrenoceptor agonists in the rabbit pulmonary artery. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1975;291(1):55–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00510821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strandhoy J. W., Morris M., Buckalew V. M., Jr Renal effects of the antihypertensive, guanabenz, in the dog. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 May;221(2):347–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strandhoy J. W., Morris M., Steg B. D., Buckalew V. M., Jr Synergistic effect of modest volume expansion on the diuretic and natriuretic action of guanabenz. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Aug;226(2):419–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- U'Prichard D. C., Snyder S. H. Distinct alpha-noradrenergic receptors differentiated by binding and physiological relationships. Life Sci. 1979 Jan 1;24(1):79–88. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90283-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winer N., Chokshi D. S., Walkenhorst W. G. Effects of cyclic AMP, sympathomimetic amines, and adrenergic receptor antagonists on renin secretion. Circ Res. 1971 Sep;29(3):239–248. doi: 10.1161/01.res.29.3.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambraski E. J., Dibona G. F., Kaloyanides G. J. Effect of sympathetic blocking agents on the antinatriuresis of reflex renal nerve stimulation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Aug;198(2):464–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


