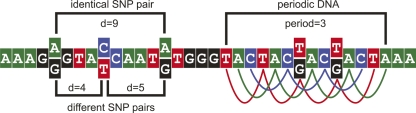
Figure 1.
Definitions of distances in SNP pairs and an example of periodic DNA. Distances are calculated between all SNPs, thus the figure shows three pairs with three distances. The distance (d) between any two SNPs is defined as the positive difference between the two genomic SNP positions, for example, d = 1 indicates neighboring SNPs. The distance definition is chosen such that distances are additive between neighboring SNPs. Identical SNP pairs are defined as two SNPs each with identical alleles (here SNP1: A/G, SNP2: A/G, d = 9). Different SNP pairs are defined as two SNPs with different alleles (here SNP1: A/G, SNP2: C/T, d = 4; SNP1: C/T, SNP2: A/G, d = 5). To the right, an example of periodic DNA is shown. The period is 3, and it is shown that SNPs are allowed in the pattern.