Fig. 5.
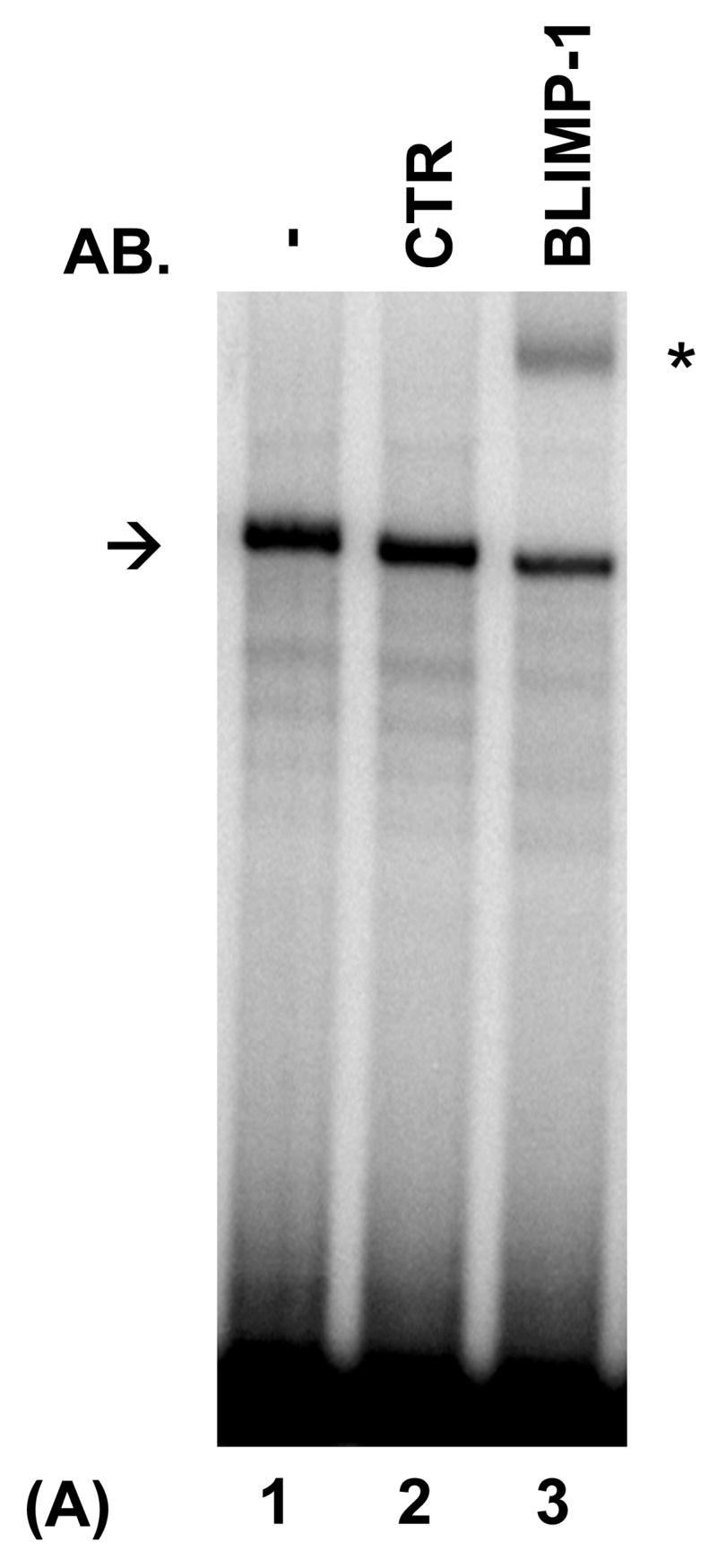
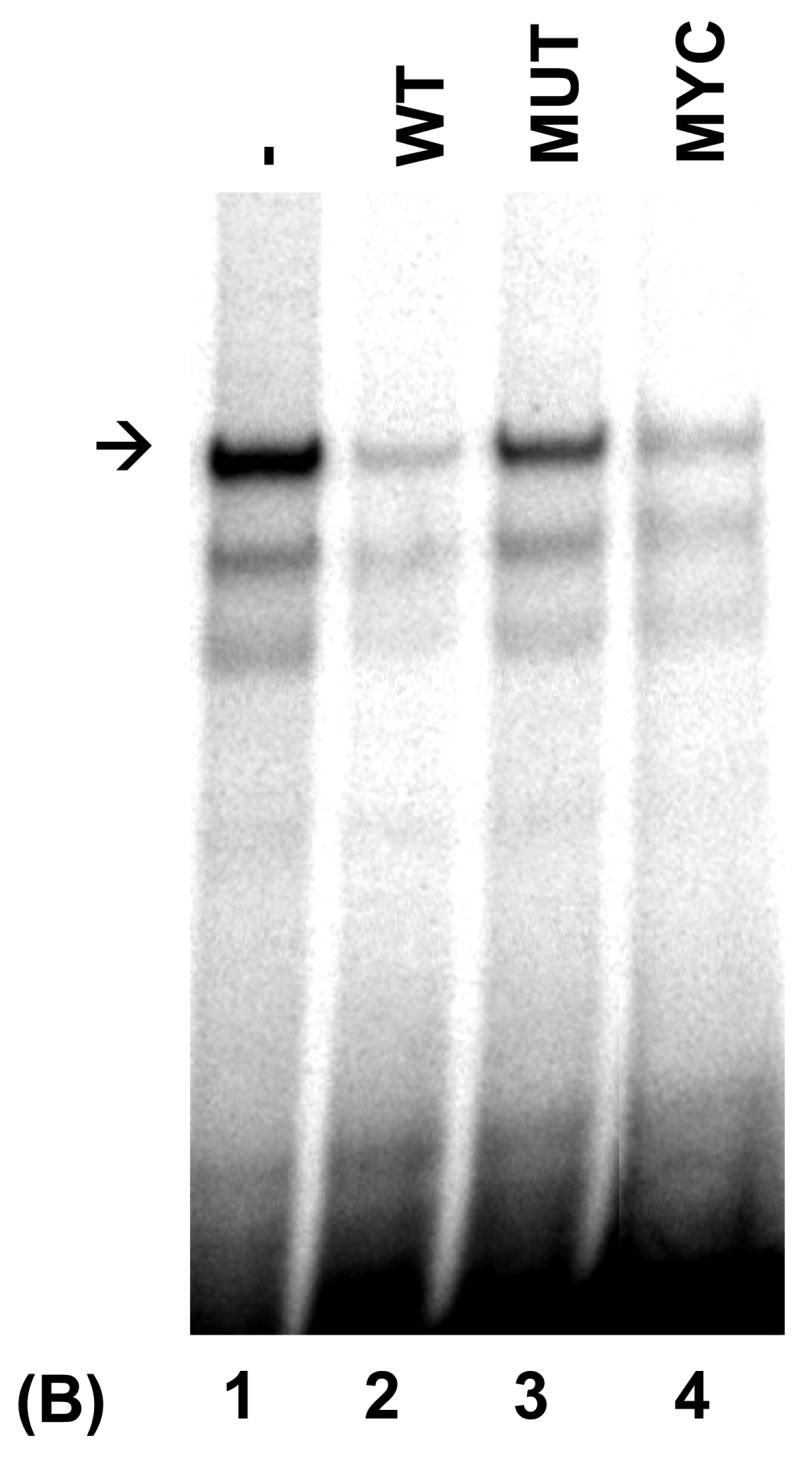
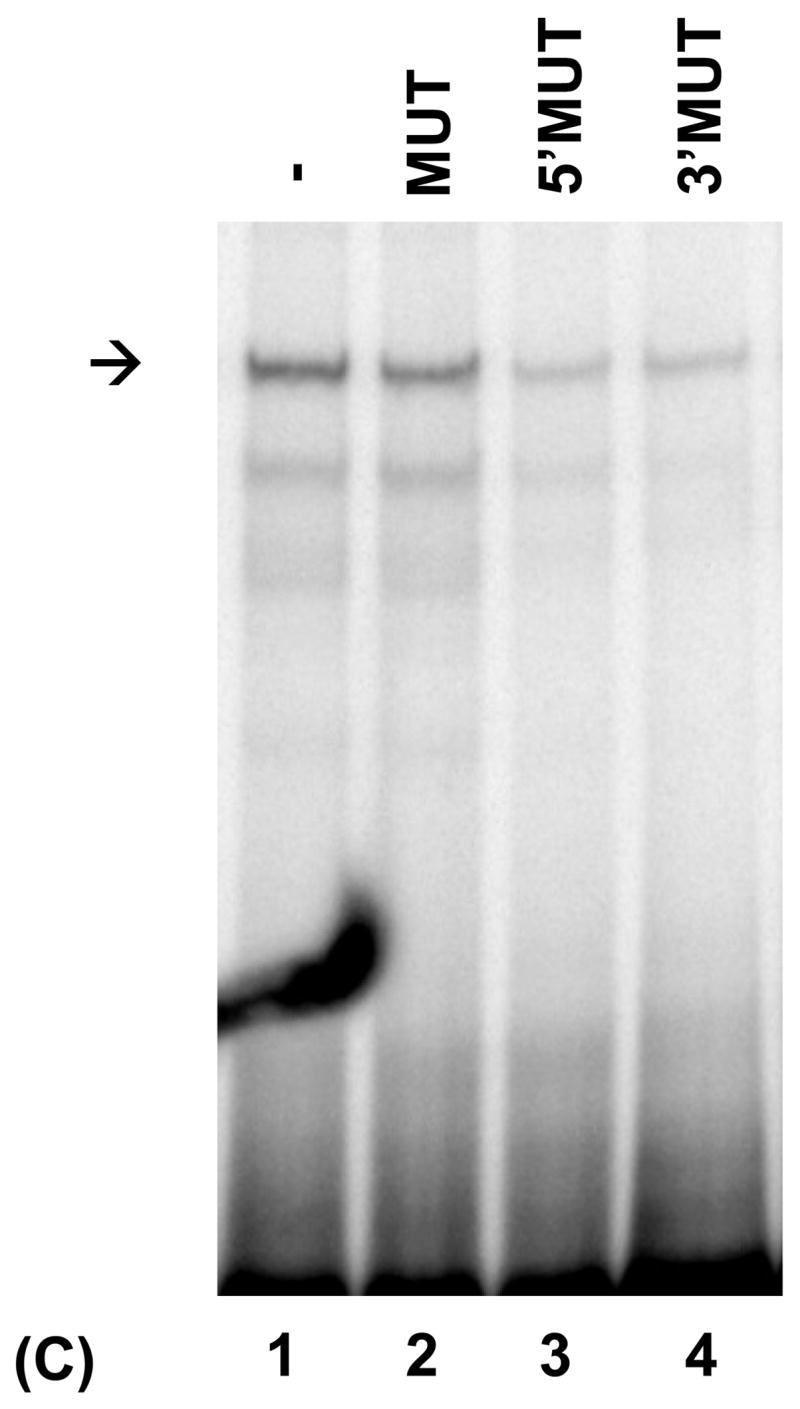
PRDI-BF1β, an alternative isoform of PRDI-BF1 expressed in myeloma cells, binds the CIITA type IV promoter. (A) EMSA analysis performed using the wild-type CIITA pIV probe and in vitro translated PRDI-BF1β protein demonstrates one predominant protein complex (lane 1, arrow). Preincubation with an antibody (AB.) specific for Blimp-1, which recognizes an epitope that is conserved in PRDI-BF1β, results in a shift in the mobility of this complex (lane 3, asterisk). Preincubation with an IgG1 isotype control (CTR) does not result in a supershifted complex. (B) EMSA analysis of in vitro translated PRDI-BF1β protein, using the wild-type CIITA pIV probe and cold competitors. The specific complex (arrow) is diminished by incubation with wild-type CIITA pIV oligonucleotide (WT, lane 2) or an oligonucleotide bearing the Blimp-1 binding site of the c-Myc promoter (MYC, lane 4), but is not diminished by a CIITA pIV oligonucleotide with a mutated IRF-E site (MUT, lane 3). (C) EMSA analysis using in vitro translated PRDI-BF1β protein, the wild-type CIITA pIV probe and mutated cold competitors. The cold competitors include a CIITA pIV oligonucleotide with a mutation that disrupts both GAAAG motifs in the IRF-E site (MUT), and oligonucleotides with mutations that disrupt the first (5′MUT) or second (3′MUT) GAAAG motif. Incubation with either of the cold competitor oligonucleotides in which a single unmutated GAAAG motif is present is capable of diminishing the formation of the specific complex (arrow), compare lanes 3 and 4 with lanes 1 and 2.
