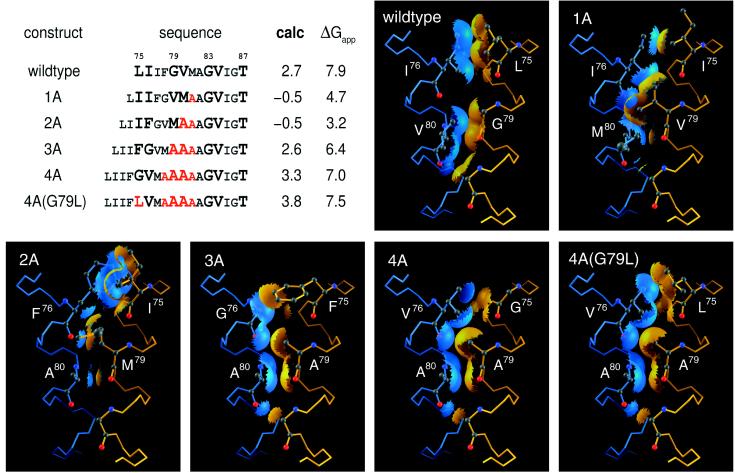
Figure 6.
Sequences, inferred structures, and calculated and experimental dimer stabilities for insertion mutants of GpA. Sequences of GpA fusion proteins from ref. 23 are aligned by using Thr-87. Inserted or mutated residues are in red; residues aligned with the motif are in large type. Numbering of residues in the panels corresponds to their positions in the motif alignment, not to numbering in the construct. Values for calc and ΔGapp values are computed by using Eq. 4 and 5, respectively. The six panels show the packing at the interface resulting from building these sequences into the GpA wild-type backbone geometry. Molecular surfaces are displayed for wild type, 3A, 4A, and 4A(G79L), where one monomer approaches within 1.5 Å of the other and serve to depict the close packing across the interface. For sequences 1A and 2A, clashes are created upon building in the residues, and the surfaces serve to highlight these steric collisions. (wildtype) The wild-type residues Leu-75, Ile-76, Gly-79, and Val-80 exhibit excellent intermonomer packing. (1A) Introducing Val at position 79 of the motif generates a steric clash. (2A) Either Met at position 79 or Ile at position 75 will clash with any rotamer of the Phe at position 76. (3A) Four weakly disruptive single mutations are placed into motif positions, but our model indicates that these should have compensatory interactions with one another. The Ala at position 79 would clash slightly in the wild-type sequence as described previously (14), but having Ala replace Val at position 80 eliminates this clash and generates good packing. The Phe side chain of position 75 would need to swing away from the interface to avoid a clash in a wild-type context, but the space afforded by the Gly at position 76 enables close packing between the Phe side chain and the backbone of the opposite monomer. (4A) Interactions between Ala residues at 79 and 80 are favorable, as for 3A. Placing Val in position 76 reintroduces the favorable interactions obtained in the wild type by having a β-branched residue at the dyad. (4A(G79L)) As 4A, except that a (wild-type) Leu is placed at position 75 in a new geometry. The rank order of the calculated and predicted dimerization propensities compare well, showing that the stabilities of these mutants can be predicted by using the same rules as were used for the single-point mutants.