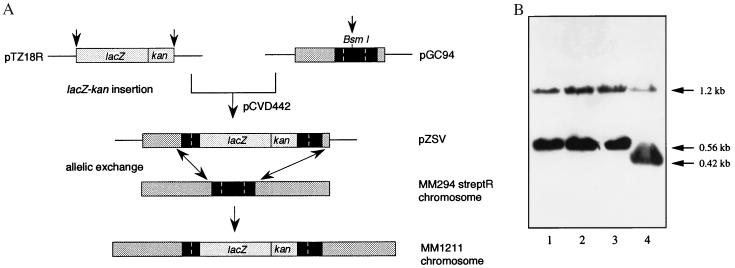
Figure 2.
Genetic analysis of aqpZ knockout in E. coli. (A) Construction of an aqpZ∷lacZ transcriptional fusion gene on the E. coli MM294-streptR chromosome. The aqpZ gene is represented by the solid rectangle with the ORF bracketed by vertical dashed lines. A promoterless 3.9-kb lacZ-kan cartridge was inserted into the BsmI site of the aqpZ gene carried by the pZSV suicide plasmid. This yielded a aqpZ∷lacZ-kan fusion gene that was used to replace the aqpZ gene in the wild-type chromosome (MM294 streptR) by a double allelic recombination. The resulting aqpZ knockout strain, MM1211, contains the intact aqpZ promoter linked to lacZ-kan. (B) Southern analysis of disrupted aqpZ gene. Genomic DNAs from wild-type E. coli strains MC4100 (lane 1), MM294 (lane 2), MM294 streptR (lane 3), and the aqpZ gene disruption construct MM1211 (lane 4) were cut with BglI and AvaII and electrophoresed into agarose gel. The DNA fragments were transferred to a membrane and hybridized at high stringency with a probe containing the entire coding region of aqpZ labeled with Digoxigenin.