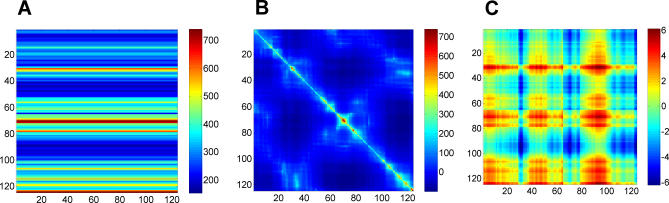
Figure 4. Physical Meaning of Hitting Times.
Decomposing the hitting time H(j,i) matrix from Figure 1A into (A) one-body, (B) two-body, and (C) three-body terms, such that summation of these three matrices will reproduce the matrix in Figure 1A. The one-body term involves the fluctuations of only the destination node, apparent by the horizontal stripes seen (A). From the scale of this plot, it is easy to infer that the one-body term dominates the overall computation of the hitting time. However, the source node can modulate the hitting time to the destination node depending on the cross-correlations between the fluctuations of the two nodes (B). (C) reveals the contribution from the three-body terms to be negligibly small.