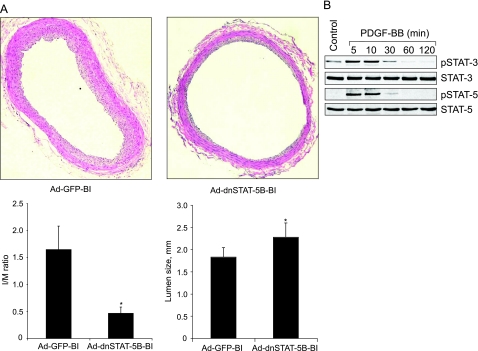
Figure 9.
A: Blockade of STAT-5B signaling inhibits balloon injury-induced neointima formation. All treatment conditions were the same as in Figure 6 except that 2 weeks after balloon injury, rats were sacrificed, arteries were isolated and fixed, and cross-sections were made and stained with H&E. After morphometry analysis, I:M ratios and lumen sizes were calculated. Top shows the representative pictures of balloon-injured Ad-GFP- or Ad-dnSTAT-5B-transduced carotid artery cross sections that were stained with H&E. The bar graphs at the bottom show the quantitative analysis of the I/M ratios and lumen sizes of the balloon-injured Ad-GFP- or Ad-dnSTAT-5B-transduced rat carotid arteries. *P < 0.05 versus Ad-GFP (n = 6). B: PDGF-BB stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of both STAT-3 and STAT-5 in HASMCs. Quiescent HASMCs were treated with and without PDGF-BB (20 ng/ml) for the indicated time periods, and cell extracts were prepared. Cell extracts containing an equal amount of protein from control and each time period of PDGF-BB treatment were analyzed by Western blotting for tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT-3 and STAT-5 using their phosphospecific antibodies.