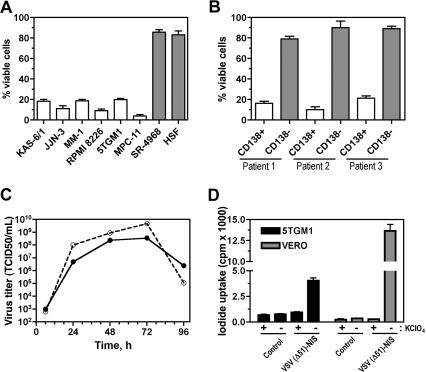
Figure 2.
VSV(Δ51)-NIS virus has in vitro antimyeloma activity and VSV(Δ51)-NIS–infected cells can concentrate radioactive iodine. For cytotoxicity studies (A,B) cells were mock-infected or infected with VSV(Δ51)-NIS (MOI = 1.0) for 30 minutes at 37°C and MTT assay was performed 48 hours after infection. Experiments were performed in triplicate and cell death is expressed as relative percentage viability compared with untreated control. Bars represent mean plus or minus a SEM. (A) Cytotoxicity of VSV(Δ51)-NIS on myeloma cell lines (human and mouse), a mouse bone marrow stromal cell line (SR-4987), or human skin fibroblasts. (B) Specific cytotoxicity of VSV(Δ51)-NIS on primary CD138-positive myeloma cells versus CD138-negative normal bone marrow progenitor cells. (C) One-step growth curves for VSV(Δ51)-NIS (●) and VSV(Δ51)-GFP (ϒ) in 5TGM1 cells. Cells were infected with VSV(Δ51)-NIS (MOI = 1.0) for 30 minutes at 37°C, supernatants were harvested at various time points, and virus titers (TCID50/mL) were determined on Vero cells. (D) In vitro Na125I uptake in 5TGM1 or Vero cells infected with VSV(Δ51)-NIS, with or without KClO4. The data are presented as cpm per 105 cells. Experiments were performed in triplicate (mean ± SEM) and are representative of 3 independent experiments.