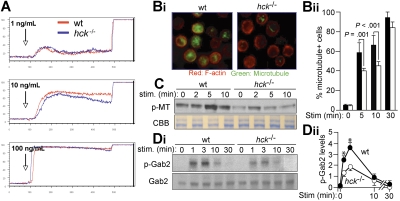
Figure 3.
Hck deficiency results in impaired microtubule formation associated with reduced Gab2 phosphorylation. (A) IgE-sensitized WT and hck−/− BMMCs were stimulated with the indicated concentrations of antigen at the indicated points and with 2.5 μg/mL ionomycin 400 seconds later. Ca2+ flux was measured by flow cytometry. Representative results from 3 experiments are shown. (B) IgE-sensitized cells were stimulated with 100 ng/mL DNP23-HSA for 5, 10, and 30 minutes. Immunofluorescence analysis for F-actin (stained by rhodamine-phalloidin) and microtubules (stained by anti-α-tubulin) was performed. Images shown are taken from cells stimulated for 10 minutes (Bi). The percentage of microtubule+ cells is shown in panel Bii. See “Microscopy” for image acquisition information. (C) IgE-sensitized cells were stimulated with 100 ng/mL DNP23-HSA for the indicated periods (minutes). Polymeric tubulin (p-MT) in Triton-insoluble fractions was measured as described in Document S1 (top). An SDS-PAGE gel containing Triton-soluble proteins was stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue to show that comparable amounts of lysates were used for this assay. (Di) Immunoblot analysis of phospho-Gab2 (Tyr-452) in IgE/antigen-stimulated BMMCs (top panel). The same blot was reprobed with anti-Gab2 (bottom panel). Densitometric analysis was performed (Dii). Values shown in panel Dii represent means from at least 3 independent experiments at each time point. Error bars represent SEM. *Statistically significant differences between WT and hck−/− cells (P < .05 by Student t test).