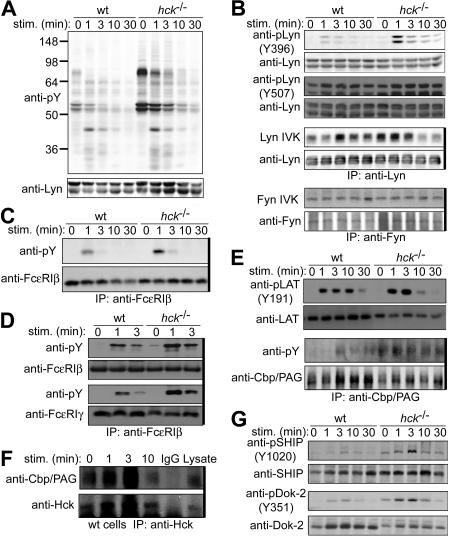
Figure 4.
Hck deficiency leads to increased Lyn activity and increased phosphorylation of Lyn phosphorylation targets. IgE-sensitized WT and hck−/− cells were stimulated with 100 ng/mL DNP23-HSA for the indicated periods. Cell lysates were either directly analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies (A,B,E,G) or first immunoprecipitated (indicated by thick vertical lines on the right of gels) with anti-FcϵRIβ mAb (C) or anti-Cbp/PAG (E,F), and followed by immunoblotting with antiphosphotyrosine mAb (C,E) or anti-Hck antibody (F). (B) Immunoprecipitated SFKs were subjected to in vitro kinase assays. (D) Cell lysates were fractionated into lipid raft and soluble compartments by sucrose density gradient ultracentrifugation. Lipid raft compartments were immunoprecipitated with anti-FcϵRIβ mAb, and followed by immunoblotting with antiphosphotyrosine mAb. Immunoprecipitated antigens were detected by reprobing the blots. Representative results from 2 experiments are shown, except for Lyn and Fyn kinase assays (B), which represent 3 experiments, and phosphotyrosine probing (A), which represent at least 4 experiments.