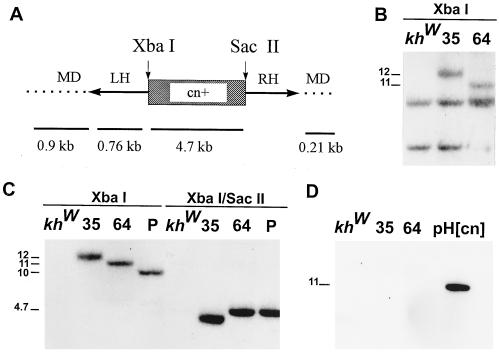
Figure 2.
(A) A representational map of the partial structure of the Hermes construct, pH[cn]. The Hermes left (LH) and right (RH) inverted terminal repeats (arrows) flank the 4.7-kb genomic fragment of D. melanogaster DNA carrying a wild-type copy of the cinnabar gene (cn+) (boxed region). This potentially mobile portion of the pH[cn] construct is flanked by M. domestica genomic DNA (MD, dotted lines). The positions of two restriction endonuclease-cleavage sites (SacII and XbaI) are indicated. The relative extents and sizes of the DNA fragments used as probes in the Southern analyses are shown below the map (numbers and solid lines). (B) Southern analysis of genomic DNA isolated from G1 progeny of transformed families 35 and 64, and the control recipient strain, khw, digested with XbaI, which cuts once in the integrated fragment, hybridized with the 0.76-kb LH-labeled fragment. Unique hybridization signals associated with insertions in families 35 and 64 are seen at 12 and 11 kb, respectively. Lower molecular weight signals corresponding to cross-hybridizing fragments are seen in the transformed families and recipient strain. (C) Southern blot analysis of genomic DNA isolated from G2 mosquitoes of families 35, 64, and the pool (P), and the recipient strain digested with either XbaI or XbaI/SacII, and hybridized with the 4.7-kb cn+ labeled fragment. High molecular weight signals corresponding to fragment lengths of 12, 11, and 10 kb are seen in the XbaI digests of DNA from families 35, 64, and the pool, respectively. The expected 4.7-kb fragment size is evident in the XbaI/SacII digest of DNA from family 64 and the pool. However, a truncated signal at 4.5 kb is seen in family 35 DNA, indicating loss of some DNA. (D) Southern blot analysis of genomic DNA isolated from G2 mosquitoes of families 35, 64, and the recipient strain, khw digested with XbaI, and hybridized with the MD-labeled fragments. The positive control is XbaI-digested pH[cn].