Figure 8.
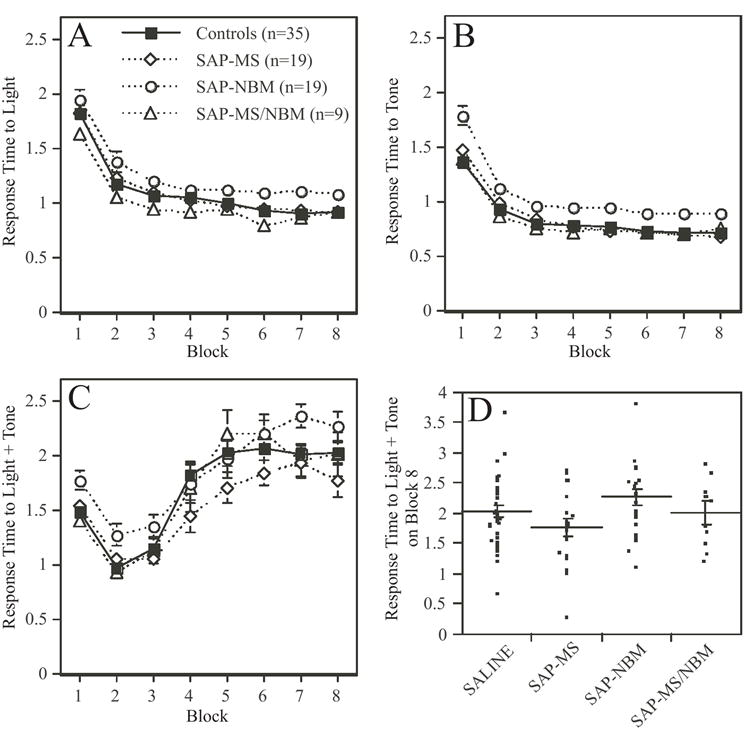
Plots summarizing the effects of the SAP lesions on response time to simple and configural stimuli during acquisition of the CA task The data are grouped into eight 3-day blocks of training. In panels A-C, each data point represents a group mean ± s.e.m. Panels A and B show the mean response time to presentation of either the light or the tone. Note that animals quickly learn to associate light or tone with food reward, as indicated by the decrease in response time. ANOVA revealed that animals in the SAP-NBM group performed slightly worse than animals in the other groups (see text for statistics). Panel C shows the mean response time to presentation of the combined stimulus of light + tone. Note that animals initially decreased their response time to the configural stimulus, but over time they increased their response time as they learned to distinguish between the lack of reward associated with responding to the configural stimulus versus the positive reward associated with responding to the simple stimuli. ANOVA revealed a significant effect of Treatment on response time to the configural stimulus, which was due to a significant difference between the SAP-MS and SAP-NBM groups. Panel D is a scatter plot showing each rat’s mean response time to the combined stimulus on Block 8 of training. Lines indicate mean ± s.e.m. Note the considerable variance in response time after 24 days of training.
