Figure 1. Sequence alignment of selected asparaginases.
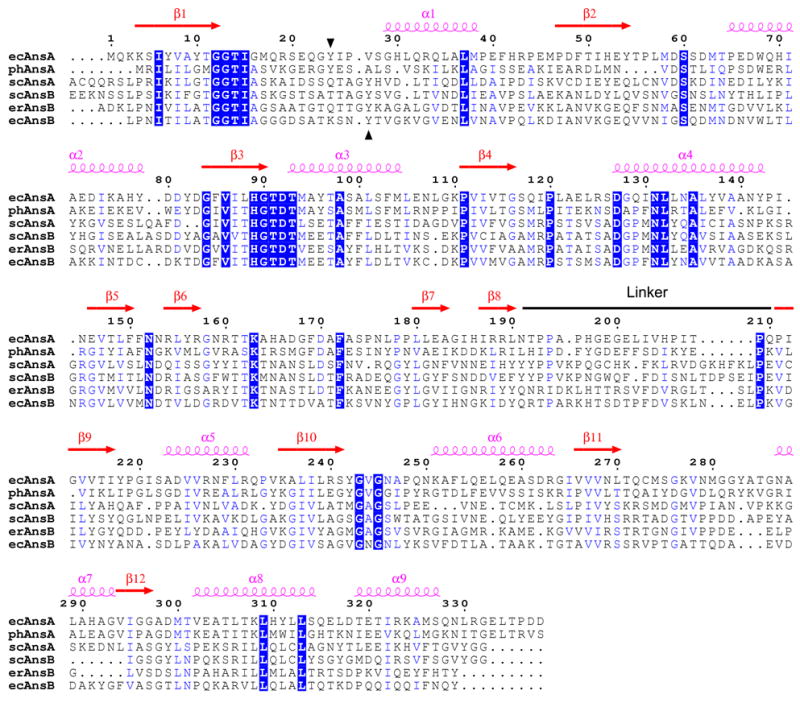
The alignment and secondary structure locations are with respect to the E. coli type I (AnsA) enzyme described in this paper. The linker region that joins the N- and C-terminal domains of the structure is indicated. Regions of sequence identity and sequence similarity are shown in blue boxes and blue text, respectively. The conserved tyrosine with a putative catalytic role is indicated by black arrowheads (residue 24 in ecAnsA). The sequences of three intracellular AnsA enzymes and three extracellular AnsB enzymes are shown; ec, E. coli; ph, Pyrococcus horikoshii; sc, Saccharomyces cerevisiae; er, Erwinia chrysanthemi. For clarity, the signal sequences at the N-termini of AnsB enzymes are not shown, and an extended N-terminal region (amino acids 1–46) in scAnsA has been removed. The figure was generated with ESPript 2.2.57
