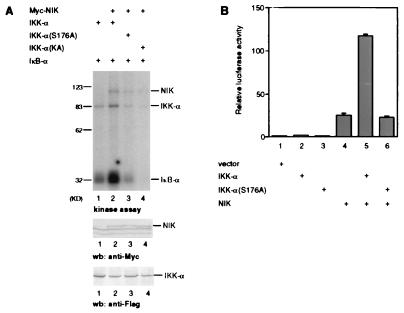
Figure 5.
Loss of IKK-α(S176A) activation by NIK. (A) Loss of IKK-α(S176A) activation by NIK in kinase assay. 293 cells were transiently transfected with expression plasmids for FLAG epitope-tagged IKK-α or IKK-α(S176A) and Myc-epitope-tagged NIK. IKK-α proteins (and coprecipitating Myc-NIK proteins) were purified with anti-FLAG antibodies, and in vitro phosphorylation reactions were carried out by using bacterially expressed IκB-α and [γ-32P]ATP. The amounts of protein used were determined by immunoblotting with anti-Myc polyclonal antibodies (Middle), and with anti-FLAG polyclonal antibodies (Bottom). (B) Loss of IKK-α(S176A) activation by NIK in an NF-κB reporter gene assay. 293 cells were transiently cotransfected with an E-selectin-luciferase reporter gene plasmid and vector control or IKK-α and NIK expression vectors as indicated. Thirty to 36 hr after transfection, luciferase activities were determined and normalized on the basis of β-gal expression. The values shown are averages (±SEM) of duplicate samples for one representative experiment.