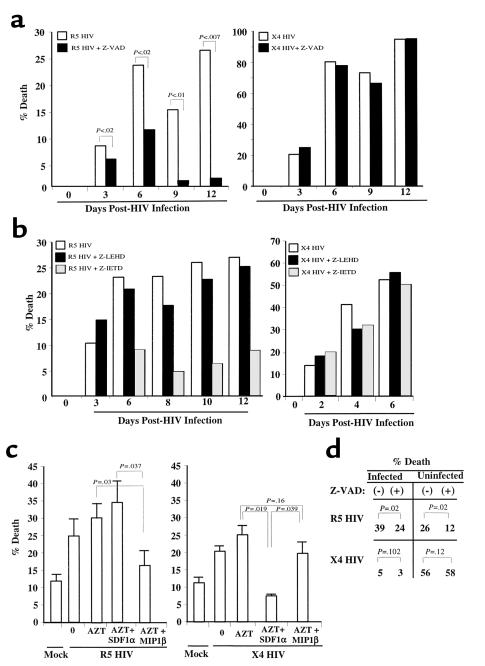
Figure 5.
Infected CD4 T-cell blasts die by chemokine receptor–dependent mechanisms. (a) PHA and IL-2–stimulated cells were infected with X4 HIV(Lav-Bru), or R5 HIV(JRFL), or mock (NI) virus. Cells were counted every 2–3 days and analyzed for cell death or by using flow cytometry changes in FSC consistent with apoptosis and for PI cell cycle. On day 6 of infection the percentage of cells infected with the R5 HIV strain shown to be apoptotic by using PI staining were 25% (– Z-VAD) and 15% (+ Z-VAD) or by FSC were 29% (– Z-VAD) and 19% (+ Z-VAD). On day 9 of infection the percentage of cells infected with X4 HIV shown to be apoptotic by PI staining were 71% (– Z-VAD) and 69% (+ Z-VAD) or by FSC were 68% (– Z-VAD) and 64% (+ Z-VAD). p24 values from the supernatants were: R5, 293(+)Z-VAD and 178(–)Z-VAD (P < 0.1); X4, 41(+)Z-VAD and 40(–) Z-VAD. SD = <10% at each data point. (b) The procedure was the same as in a, except cells were incubated in the presence or absence of caspase 8 inhibitor (Z-IETD) or caspase 9 inhibitor (Z-LEHD). (c) PHA and IL-2 stimulated and infected with R5 HIV(JR-FL), or X4 HIV(Lav-Bru), or mock infected were treated with AZT for 6 hours on day 3 of X4 HIV infection and on day 6 of R5 HIV infection. Thereafter, cells were extensively washed and incubated in the presence or absence of SDF1α or MIP1β, and cell death was analyzed 24 hours later. (d) Chemokine-receptor activation mediates death of directly HIV-infected and -uninfected CD4 T cells. PHA and IL-2–stimulated cells were infected with R5 HIV(JR-FL), or X4 HIV(Lav-Bru), or mock infected (NI). On day 4 for X4 HIV infection and day 6 for R5 HIV infection, cells were treated with AZT, and half the population was treated with Z-VAD; 18 hours later cells were stained for intracytoplasmic p24. The percentage of p24+ cells and apoptotic cells, as determined changes by FSC, were analyzed by using flow cytometry. The percentage of p24+ in the R5 HIV infection of T cells was 11% and 15% in the X4 HIV infection (+). SD = <10% at each data point.