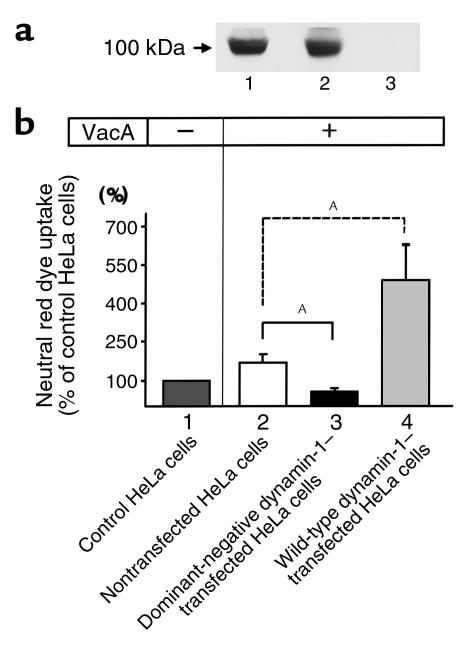
Figure 4.
Effect of stable transfection of wild-type or dominant-negative dynamin-1 on neutral red dye uptake by VacA-treated HeLa cells. (a) Stable transfection of dominant-negative or wild-type dynamin-1 in HeLa cell lines was confirmed by Western blotting. Crude lysates (30 μg protein) of HeLa cells stably transfected with dominant-negative (lane 1) or wild-type dynamin-1 (lane 2), or of nontransfected controls (lane 3), were applied to each lane for Western blotting, using an anti–dynamin-1 antibody. Wild-type or dominant-negative dynamin-1 protein was expressed in each stably transfected HeLa cell line. (b) For the neutral red dye uptake assay, cells were seeded into 96-well plates and cultured for 24 hours, then treated with VacA and incubated for a further 24 hours. After the incubation, neutral red uptake into intracellular acidic compartments was determined by measuring absorbance at 540 nm. Results are expressed as a percent of the neutral red dye uptake of nontransfected control HeLa cells without VacA treatment (lane 1). Values are means ± SE for three independent experiments with triplicate determinations. Dominant-negative dynamin-1 transfection (lane 3) significantly inhibited neutral red uptake compared with control cells (lane 2) under VacA-treated conditions. Wild-type dynamin-1 transfection (lane 4) markedly enhanced dye uptake compared with controls (lane 2) under VacA-treated conditions. AP < 0.05.