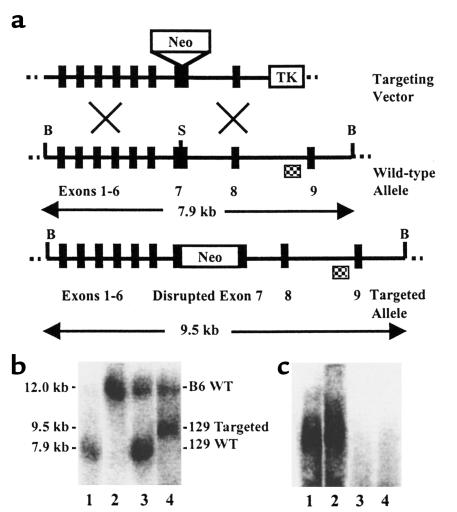
Figure 1.
Targeted disruption of the mouse MPO gene. (a) The targeting vector, wild-type MPO locus (including exons 1–9), and targeted MPO gene are shown. Exon 7 was disrupted by insertion of positive-selection marker PGK-Neo (Neo) at a BssHII (S) site. HSV-thymidine kinase (TK) served for negative selection. BglII (B) digestion sites, lengths of diagnostic BglII fragments, and external probe (checkered box) used for Southern blot analysis are indicated. (b) DNA isolated from progeny of chimeric founder male mated with C57BL/6J female was subjected to BglII digestion and Southern blot analysis. Lanes 1 and 2 contained the wild-type controls 129/SvJ DNA (lane 1) and C57BL/6J DNA (lane 2). Note the difference in band size between the two strains, indicative of a restriction fragment length variant. Strain 129/SvJ has BglII restriction enzyme sites at nucleotides 189 and 8075, yielding a 7.9-kb product, whereas C57BL/6J is lacking one of these sites, and the fragment generated represents digestion at a more distal BglII site. Restriction variants, such as this one, are due to naturally occurring nucleic acid sequence differences between inbred strains. Lanes 3 and 4 are from progeny. The larger band in both lanes is inherited from the C57BL/6J mother, and the lower band, inherited from the chimeric father, is either wild-type (lane 3) or targeted (lane 4). (c) RNA samples isolated from bone marrow from wild-type (lanes 1 and 2) and mutant (lanes 3 and 4) mice were subjected to Northern blot analysis with a human cDNA probe.