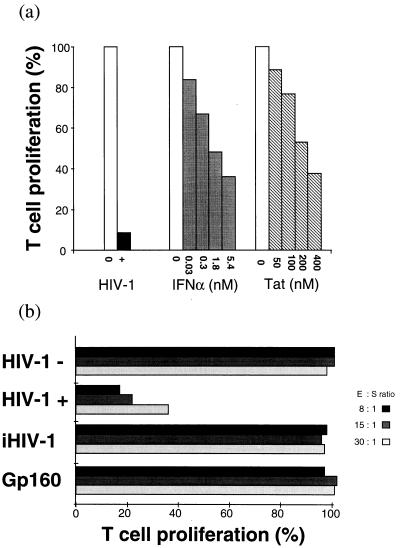
Figure 1.
HIV-1-induced immunosuppression. (a) Inhibition of T cell response induced by HIV-1, IFNα, or Tat. Fresh PBMC from seronegative donors were SEB-activated and cultured for 3 days in the absence (□) or the presence (▪) of HIV-1 (nonsyncytium-inducing strain Z96) or with varying concentrations of IFNα (IFNα2b, Biosidus). ░⃞, Fresh PBMC were pretreated at 37°C for 2 h in HL-1 medium in the absence (□) or the presence (▧) of varying concentrations of HIV-1 Tat protein. Tat-pretreated PBMC then were cultured for 3 days in a medium containing human AB serum and SEB (Right). T cell proliferation of treated PBMC (T) was compared with that of untreated PBMC (R), and results are expressed as T:R × 100. (b) HIV-1-induced generation of suppressor cells. Preparation of suppressor cells: 48-h PHA-activated PBMC infected by HIV-1 and cultured for 6 days in a medium supplemented with IL-2 (100 units/ml). Cell samples also were incubated with either heat-inactivated HIV-1 (iHIV-1) or HIV-1 gp160 and cultured in similar conditions. The assay for generation of suppressor cells was carried out by culturing for 3 days fresh effector autologous PBMC (E) stimulated by SEB in the presence (experimental samples) or the absence (control samples) of the 6-day cultured cells, tested after irradiation at varying effector/suppressor ratios. The suppressor cell activity was evaluated by T cell proliferation of effector PBMC (E) measured by 3H-thymidine incorporation. T cell proliferation in test cells (T) was compared with that of SEB-stimulated PBMC cultures used as reference cultures (R), and results are expressed as T:R × 100.