Figure 5. Effect of ionic strength on CYP2B4 and CYP1A2 mediated 7-EFC metabolism as a function of reductase concentration.
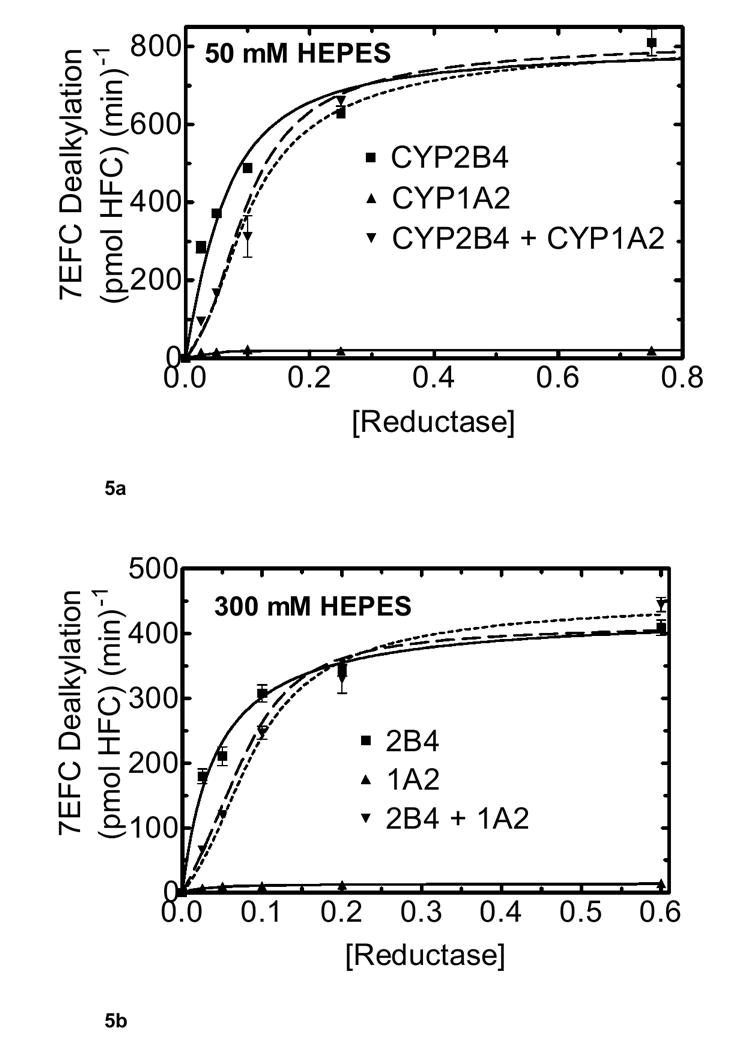
Pre-incubation conditions are the same as in figure 4 described in Materials and Methods. The final concentration of CYP2B4 and CYP1A2 each were 0.05 μM, and DLPC was 8.0 μM. The experimental data were effectively simulated using a model only allowing the formation of reductase-CYP1A2 and reductase-CYP2B4 complexes (dashed line). The dotted line shows a simulation using the model described in Scheme 2 allowing the formation of CYP2B4-CYP1A2 complexes. (a) Effect of mixed reconstitution of CYP1A2 and CYP2B4 on the reductase dependence of 7-EFC dealkylation at 50 mM HEPES. Concentrations of reductase were varied at the lower ionic strength (50 mM HEPES) buffer for CYP1A2, CYP2B4 and the mixed system. (b) Effect of mixed reconstitution of CYP1A2 and CYP2B4 on the reductase dependence of 7-EFC dealkylation (300 mM HEPES).
