Figure 2. Local Spontaneous Synaptic Activity Reduces GluR1 Diffusion.
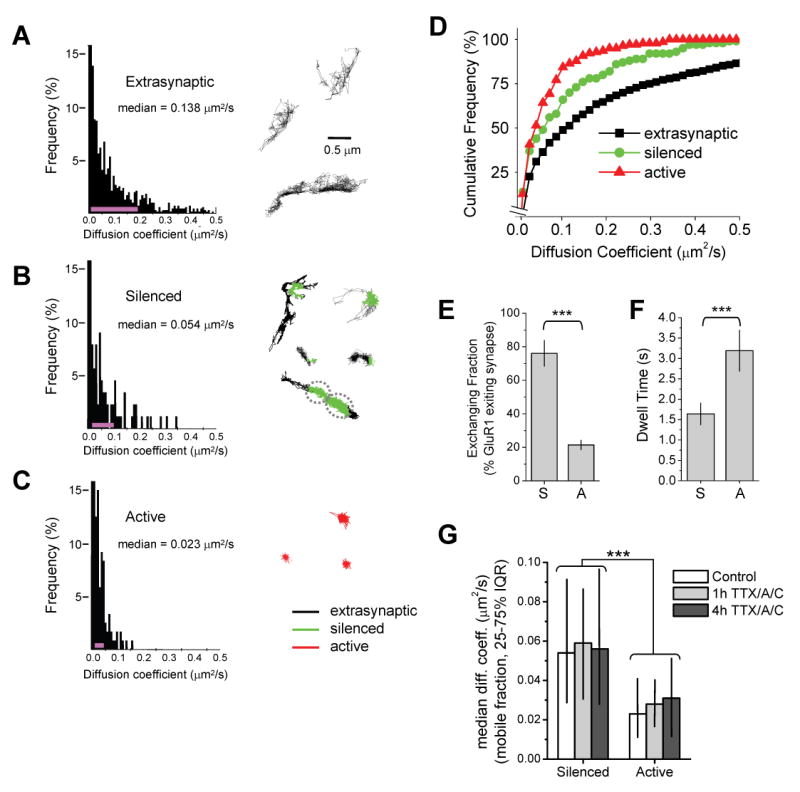
(A) Surface diffusion of extrasynaptic GluR1. Left, histogram of GluR1 diffusion coefficients (D) in the extrasynaptic plasma membrane (n = 1478 trajectories reconstructed from 69 image fields on 13 coverslips, median D value is shown). The pink line indicates the 25–75% interquartile range (IQR). Right, examples of GluR1 trajectories over extrasynaptic dendritic regions.
(B) Diffusion of GluR1 at silenced synapses. Left, histogram of GluR1 diffusion coefficients during episodes spent in inactive synapses (n = 125 trajectories reconstructed from 34 image fields on 13 coverslips, median D value is shown). Pink line, 25–75% IQR. Right, examples of GluR1 trajectories near silenced synapses (green). Trajectory color code as in (C).
(C) Diffusion of GluR1 at active synapses. Left, histogram of GluR1 diffusion coefficients during episodes spent in active synapses (n = 175 trajectories reconstructed from 26 image fields on 11 coverslips, median D value is shown). Pink line, 25–75% IQR. Right, examples of GluR1 trajectories at active synapses (red). The distributions in (A)–(C) are statistically different (p < 0.0001 for each pairwise comparison, Mann-Whitney test).
(D) Cumulative probability plot of GluR1 diffusion coefficients. GluR1 exhibits slower diffusion at active synapses relative to silenced synapses and at all synapses relative to extrasynaptic membrane.
(E) GluR1 receptors frequently exit silenced synapses. Data represent means ± SEM of the percent GluR1-QDs present at silenced (S) or active (A) synapses which leave the synapse during any portion of the 60 sec imaging period. ***p < 0.001, t-test.
(F) Exchanging GluR1 receptors remain for longer periods at active synapses. Data represent means ± SEM of the dwell times of GluR1-QDs at silenced (S) or active (A) synapses. Note that only GluR1-QDs which depart the synapse are included in the analysis. ***p < 0.001, t-test.
(G) Acute activity blockade does not alter GluR1 mobility at previously active or previously silenced synapses. Hippocampal cultures infected with synaptophysin-GFP:IRES:TetTx on DIV7 were incubated with 1 μM TTX, 50 μM D-AP5 (A), and 10 μM CNQX (C) for one or four hours before imaging on DIV15. Data represent median diffusion coefficents. IQR, interquartile range. Note that acute treatment with TTX/A/C did not alter GluR1 diffusion at either chronically silenced synapses expressing synaptophysin-GFP:IRES:TetTx or neighboring active synapses. Control, n = 125, 175 trajectories at silenced and active synapses, respectively. One hour TTX/A/C, n = 13, 11; 4 hours TTX/A/C, n = 15, 19. *** p < 0.001 for all pairwise comparisons between previously active and silenced synapses, Mann-Whitney test.
