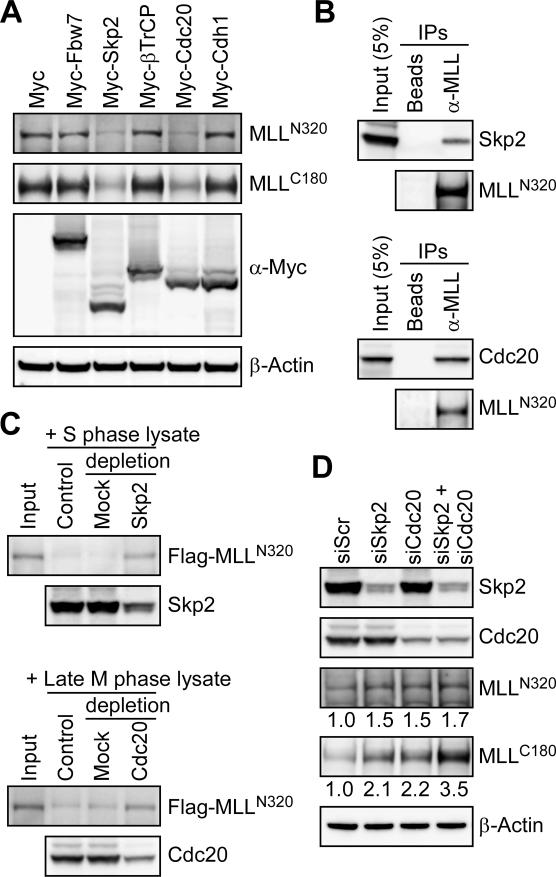
Figure 3.
The bimodal degradation of MLL is mediated by SCFSkp2 and APCCdc20. (A) Specialized substrate recognition modules (Skp2 and Cdc20) of the cell cycle E3 ligases are required for the degradation of MLL. Specific degradation of the endogenous MLL protein occurred in cells with overexpression of Skp2 or Cdc20. 293T cells were transfected with the indicated Myc-tagged substrate recognition module of cell cycle E3 ligases, and the levels of endogenous MLL were detected with the indicated anti-MLL antibodies. The level of β-actin served as a loading control. (B) MLL interacts with Skp2 and Cdc20 in vivo. Cellular lysates of 293T cells treated with MG132 were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-MLL antibody. Coprecipitated Skp2 and Cdc20 were detected by immunoblots. Protein-A beads served as a negative control. (C) In vitro degradation assays confirm the direct recognition and subsequent destruction of MLL by SCFSkp2 and APCCdc20 in S and late M phases, respectively. Immunoprecipitated Flag-MLL was incubated with the indicated cellular lysates obtained from synchronized HeLa cells at 30°C for 30 min before being subjected to Western blot analyses. Anti-Skp2 or anti-Cdc20 immunoprecipitation was performed to deplete SCFSkp2 or APCCdc20 from the indicated lysates. Mouse IgG was used as mock depletion. (D) Knockdown of Skp2 and/or Cdc20 leads to the accumulation of MLL protein. HeLa cells were transfected with the indicated siRNA specific for Skp2 or Cdc20. Protein levels of endogenous Skp2, Cdc20, and MLL were analyzed by Western blots at 72 h after transfection and quantified using ImageGauge software (FujiFilm). The level of β-actin served as a loading control, and the expression of MLL in control knockdown (siScr, si scramble) was arbitrarily assigned as 1.0.