Figure 1.
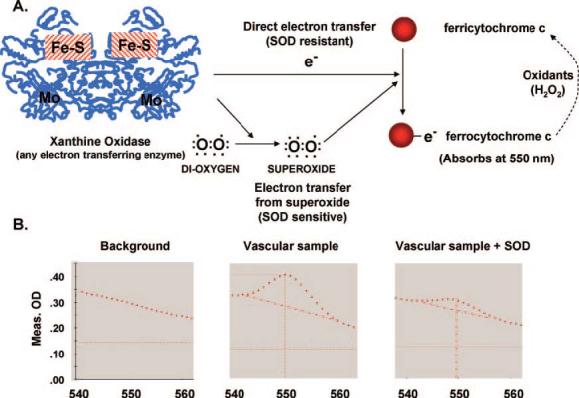
Detection of O2•− by reduction of ferricytochrome c. A, Various enzymes (shown as an example is xanthine oxidase) can generate electrons, which can directly reduce cytochrome c and also reduce oxygen leading to O2•− formation. Superoxide, in turn, can donate its electron to ferricytochrome c, leading to formation of ferrocytochrome c. SOD is used to differentiate between a direct reduction of ferricytochrome c vs reduction mediated by O2•−. B, Reduction of ferricytochrome c can be detected at 550 nm absorbance, using 540 and 560 nm as isosbestic points.
