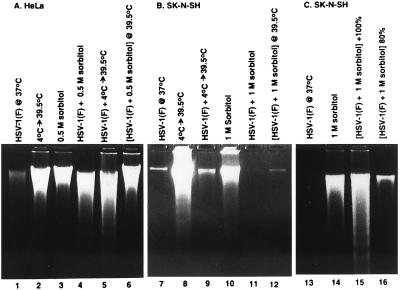
Figure 2.
Photograph of agarose gels containing electrophoretically separated low molecular weight DNA fractions from mock-infected or HSV-1(F)-infected cells and stained with ethidium bromide. Subconfluent HeLa (A) or SK-N-SH cells (B) or subconfluent and confluent SK-N-SH cells (C) were mock-infected (lanes 2, 3, 8, 10 and 14) or infected with HSV-1(F) (lanes 1, 4–7, 9, 11–13, 15 and 16), treated by temperature shift (4°C → 39.5°C) or osmotic shock (0.5 M or 1 M sorbitol) and incubated for 5 hr (sorbitol-treated cells) or for 36 hr (other cultures) at 37°C unless otherwise indicated. 2 × 106 cells per sample were collected, rinsed in PBS and lysed in a solution containing 10 mM Tris⋅HCl (pH 8.0), 10 mM EDTA and 0.5% Triton X-100 and centrifuged at 14,000 rpm for 30 min in an Eppendorf microcentrifuge to pellet chromosomal DNA. The supernatant fluids were digested with 0.1 mg/ml RNase A at 37°C for 1 hr and then with 1 mg/ml proteinase K at 50°C in the presence of 1% SDS, extracted with phenol and chloroform, precipitated in cold ethanol and subjected to electrophoresis in 2% agarose gels containing 5 μg/ml ethidium bromide. DNA was visualized by UV light transillumination and photographed with the Eagle Eye II (Stratagene).