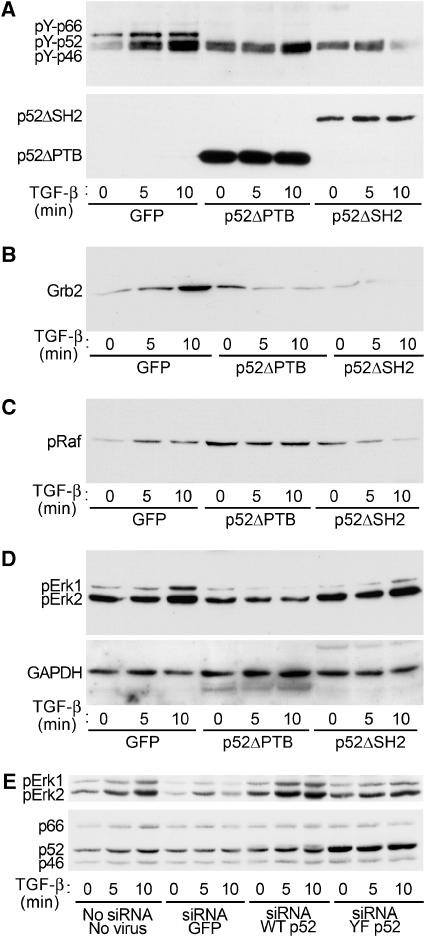
Figure 8.
Erk activation by TGF-β is inhibited by inactive ShcA mutants and ShcA downregulation. 3T3-Swiss cells were infected with adenoviruses expressing GFP (control), HA-tagged p52ShcA lacking the PTB domain (p52ShcAΔPTB), or HA-tagged p52ShcA lacking the SH2 domain (p52ShcAΔSH2). Cells were then stimulated with TGF-β for the indicated times and lysed. (A) TGF-β-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of endogenous ShcA is attenuated by expression of p52ShcA truncations. Endogenous ShcA was immunoprecipitated and subjected to phosphotyrosine Western analysis (above). HA immunoblotting of this membrane confirmed expression of p52ShcA truncations and equivalent precipitation efficiency (below). (B) TGF-β-induced Grb2 association with endogenous ShcA is attenuated by p52ShcA truncations. The membrane in (A) was subjected to Grb2 Western analysis. (C) TGF-β-induced Raf phosphorylation is attenuated by p52ShcA truncations. Cell lysates from the experiment shown in (A) were subjected to phosphoRaf Western blot. (D) TGF-β-induced Erk phosphorylation is attenuated by p52ShcA truncations. The membrane shown in (C) was subjected to phosphoErk1/2 Western blot (above). The membrane was reprobed for GAPDH to confirm equivalent loading (below). (E) TGF-β-induced Erk activation is attenuated by ShcA silencing and restored by ectopic expression of wild-type, but not mutant p52ShcA. 3T3-Swiss cells were exposed to an siRNA targeted to the common region of ShcA together with adenoviruses encoding either green fluorescent protein (GFP), wild-type p52ShcA, or p52ShcA in which the Grb2 binding sites are mutated. Both p52ShcA constructs incorporate a silent mutation in the siRNA target site. PhosphoErk immunoblot of cells stimulated with TGF-β for the indicated times (above). ShcA immunoblot confirming partial downregulation and virus-mediated expression (below).