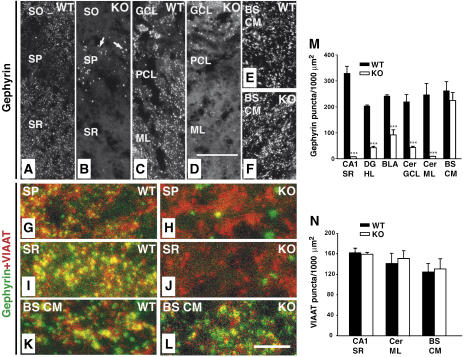
Figure 3.
Region-specific reduction of synaptic gephyrin staining in the Cb KO CNS. (A–L) Sections from adult Cb KO mice and their WT littermates were stained with gephyrin and VIAAT antibodies. (A, B) The punctate staining of sections from KO animals for gephyrin was strongly reduced in the CA1 region of SR and SO as compared with WT sections. Note the significant increase of gephyrin deposits (arrows in B) in the SP of KO sections (A). (C, D) A strong reduction of gephyrin immunoreactivity was also observed in cerebellar regions (GCL, PCL, ML) of Cb KO animals. (E, F) BS CM sections in contrast showed similar densities of gephyrin puncta in both WT and KO animals. (G–L) Double immunostainings of gephyrin and VIAAT puncta in the SP (G, H) and SR (I, J) of the hippocampus, and in brainstem (K, L) of WT and Cb KO mice. Note that, in contrast to the loss of gephyrin puncta seen in (H, J), VIAAT immunoreactivity was unaffected by Cb deficiency (H, I). Scale bars, 32 μm (A–F), 16 μm (G–L). (M, N) Quantification of gephyrin and VIAAT immunoreactivities. For both genotypes, each bar corresponds to mean values (±s.e.m.) obtained with sections from 3–4 individual brains (***P<0.001; Student's t-test). SO, stratum oriens; SP, stratum pyramidale; SR, stratum radiatum; GCL, granule cell layer; PCL, Purkinje cell layer; Cer ML, molecular layer of cerebellum; BS CM, caudal medulla of the brainstem; DG HL, hilus of the dentate gyrus; BLA, basolateral amygdala.