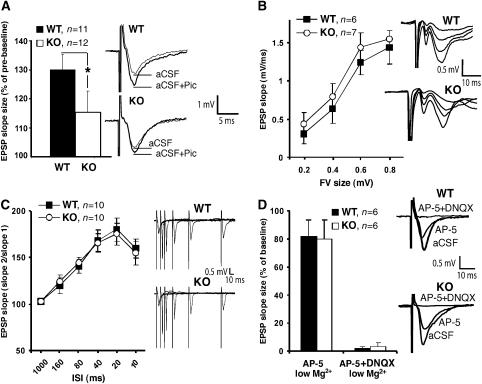
Figure 6.
Analysis of fEPSPs in the hippocampal CA1 region. (A) Left: fEPSP slope size was significantly increased by bath-application of 100 μM picrotoxin. This enhancement was significantly larger in WT as compared with Cb KO mice (*P<0.05; two-tailed Student's t-test). Right: sweeps from individual experiments before (aCSF) and after application of picrotoxin (aCSF+Pic), averaged over three trials. (B) Left: fEPSP slope size at various stimulus intensities (FV: fiber volley). Right: series of original traces recorded from WT and Cb KO slices. (C) Left: paired-pulse facilitation of the fEPSP at various interstimulus intervals (ISI) from Cb KO and WT slices. Right: single sweeps for WT and Cb KO mice recorded at 10–160 ISI. (D) Left: NMDA receptor and AMPA receptor contributions to the fEPSP recorded in the presence of the indicated antagonists under low (0.5 mM) Mg2+ conditions. Right: original traces from individual experiments. In panels A−C, there were no significant differences between KO and WT slices (P>0.1; Student's t-test). All values represent means±s.e.m.