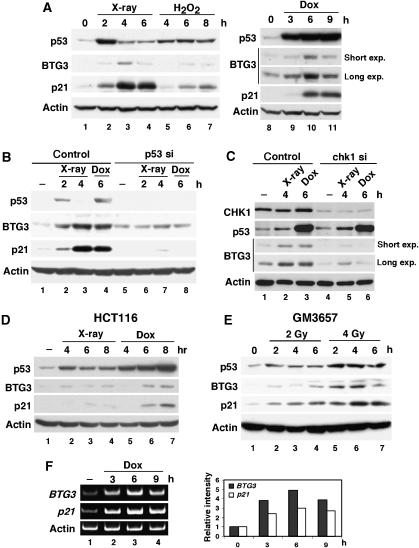
Figure 4.
BTG3 protein is induced by DNA damage in a p53-dependent manner. (A) BTG3 in LNCaP cells is induced by various DNA damage agents. Cells were treated with 8 Gy of X-ray (lanes 2–4), 0.5 mM of H2O2 (lanes 5–7) or 1 μM of doxorubicin (lanes 9–11), and then collected at the indicated time points. The amounts of p53, p21, BTG3 and actin were determined by Western blotting using appropriate antibodies. (B) p53 is required for the DNA damage-induced expression of BTG3. LNCaP cells were transfected with control or p53 siRNA, and lysates were then prepared and analyzed as described in panel A. (C) Induction of BTG3 by DNA damage is CHK1-dependent. CHK1 in LNCaP cells was first downregulated using specific siRNA, and the induction of BTG3 protein was analyzed as in panel B. (D, E) DNA damage-induced expression of BTG3 in HCT116 colorectal carcinoma cells (D) and GM3657 lymphoblastoid cells (E). Cells were treated and analyzed as in panel A, except that 0.5 μM doxorubicin (Dox) was used. (F) Expression of the BTG3 and the p21 transcripts after doxorubicin treatment as determined by semi-quantitative RT–PCR. The bar graphs on the right represent the results of quantification. Short and long exposure (exp.) on BTG3 expression were both presented in panels A and C.