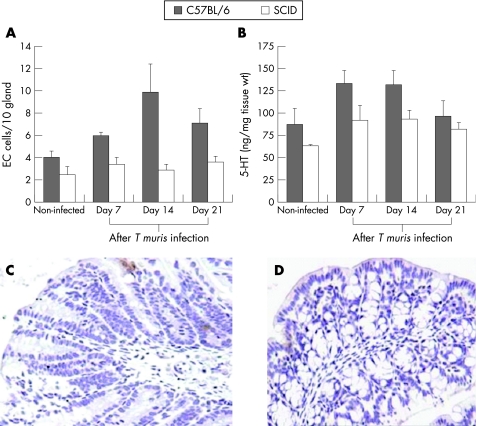
Figure 2 Severe combined immunodeficient (SCID) mice exhibited markedly lower numbers of enterochromaffin (EC) cells and lower amounts of 5‐hydroxytryptamine (5‐HT) after Trichuris muris infection than wild‐type controls. SCID mice (on C57BL/6 background) and control C57BL/6 mice were infected orally with 300 eggs of T muris and were killed on different days after infection to study 5‐HT‐expressing EC cells and the amount of 5‐HT in the colon. (A) Number of EC cells in the colon of non‐infected and infected SCID and C57BL/6 mice. (B) Amount of 5‐HT in the colonic tissue of non‐infected and infected SCID and C57BL/6 mice. (C) Representative micrograph showing 5‐HT‐expressing EC cells in the colon of non‐infected SCID mice. (D) Representative micrograph showing 5‐HT‐expressing EC cells in the colon of T muris‐infected SCID mice on day 14 after infection. Each bar represents mean (SEM) from five mice. Two‐way analysis of variance revealed significant difference in numbers of EC cells and the amount of 5‐HT between the SCID and C57BL/6 mice after T muris infection.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.