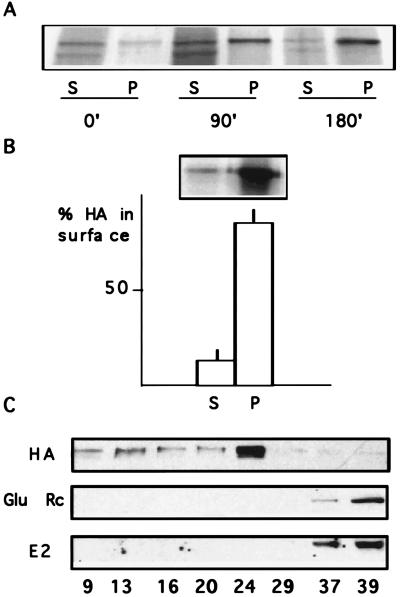
Figure 2.
HA insolubility in stage 5 neurons. (A) HA insolubility during the biosynthetic pathway. FPV-infected stage 5 neurons were metabolically labeled. After chases of 0, 90, or 180 min the cells were extracted with 20 mM CHAPS at 4°C and centrifuged. The amount of HA present in supernatants (S) and pellets (P) was determined by 10–20% SDS/PAGE and autoradiography. The mature form of HA becomes more and more insoluble with time. The lower-molecular-weight band present in the supernatants corresponds to the immature form of HA that remains in the ER. (B) HA insolubility on the surface. FPV-infected stage 5 neurons were biotinylated, and were CHAPS extracted. The resultant supernatants (S) and pellets (P) were analyzed by SDS/PAGE and autoradiography. Almost all surface HA is detergent-insoluble (87%). The graphic shows the data expressed as percent of the total surface HA and mean values ±SD from three different experiments. (C) Isolation of detergent-insoluble complexes. TX-100 extracts of stage 5 neurons infected with FPV (HA), noninfected (Glu Rc), or infected with SFV (E2) were prepared at 4°C and centrifuged to equilibrium in a sucrose gradient. Fractions of equal volume were collected and the amount of sucrose was determined with a refractometer (numbers at the bottom indicate percentage of sucrose). The fractions were analyzed by Western blot by using the following antibodies: anti-HA (HA), anti-AMPA glutamate receptor subunit 1 (Glu Rc), and anti-E2 (E2). HA from stage 5 cells is found in the lighter fractions (24–9% sucrose), revealing its interaction with lipids, whereas the dendritic proteins glutamate receptor and the viral E2 are found in the high density fractions (37 and 39% sucrose).