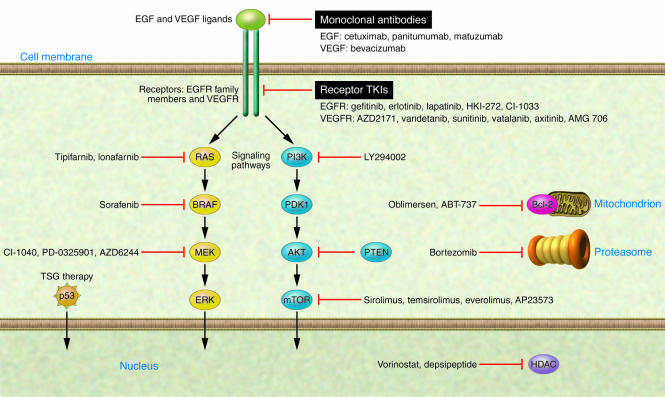
Figure 1. Novel therapies targeting key oncogenic pathways in lung cancer.
Several of the signaling and cell physiology pathways that are abnormal in lung cancer are depicted schematically along with drugs targeting components of these abnormal pathways. These drugs specifically target important molecules and pathways involved in lung cancer cell proliferation, inhibition of apoptosis, angiogenesis, and invasion and are currently in clinical trials for lung cancer. These include agents specifically inhibiting components of EGFR and other family members (such as ERBB2/Her2) and/or VEGFR pathways (with monoclonal antibodies and receptor TKIs or with inhibitors of key downstream pathway mediators such as the RAS/RAF/MEK or PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway). Other agents in development include tumor suppressor gene (TSG) therapies, inhibitors of antiapoptotic proteins such as Bcl-2, HDAC inhibitors targeting the multiple epigenetic changes found in lung cancer, and proteasome (Pr) inhibitors. PDK1, pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase isozyme 1; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog.