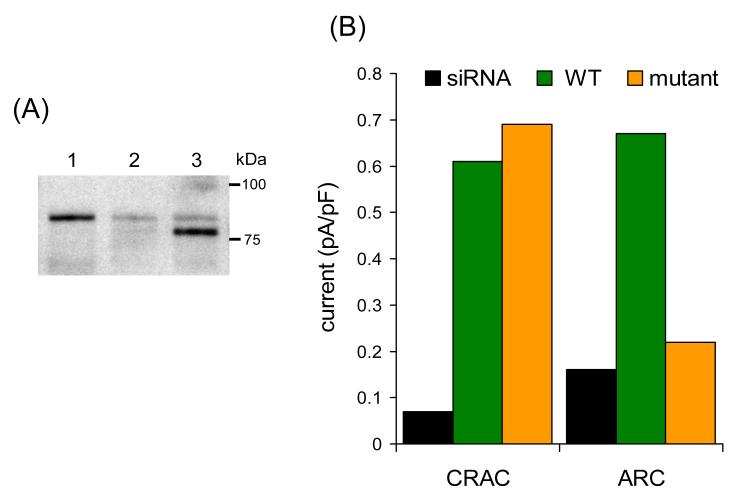
Fig. 3.
Expression of a siRNA-resistant N-glycosylation mutant STIM1 in siRNA-transfected cells selectively inhibits ARC channel activity. (A) A representative Western blot showing the expression of the N-glycosylation mutant STIM1 in siRNA-transfected cells. Lane 1 represents STIM1 in control cells, lane 2 STIM1 in cells transfected with the STIM1 siRNA, and lane 3 is the siRNA-resistant N-glycosylation mutant STIM1 expressed in siRNA-transfected cells. The glycosylation mutant runs at a lightly lower molecular weight to the endogenous STIM1, which is markedly reduced in the siRNA-treated cells. (B) Currents via CRAC channels and ARC channels recorded in the siRNA-treated cells (siRNA – black), in siRNA-treated cells expressing an siRNA-resistant wild-type STIM1 (WT – green), and in siRNA-treated cells expressing an siRNA-resistant N-glycosylation mutant STIM1 (mutant – brown). Currents are represented as the mean inward current density at –80 mV. Data redrawn from [21].