Fig. 1. Classic BER pathway.
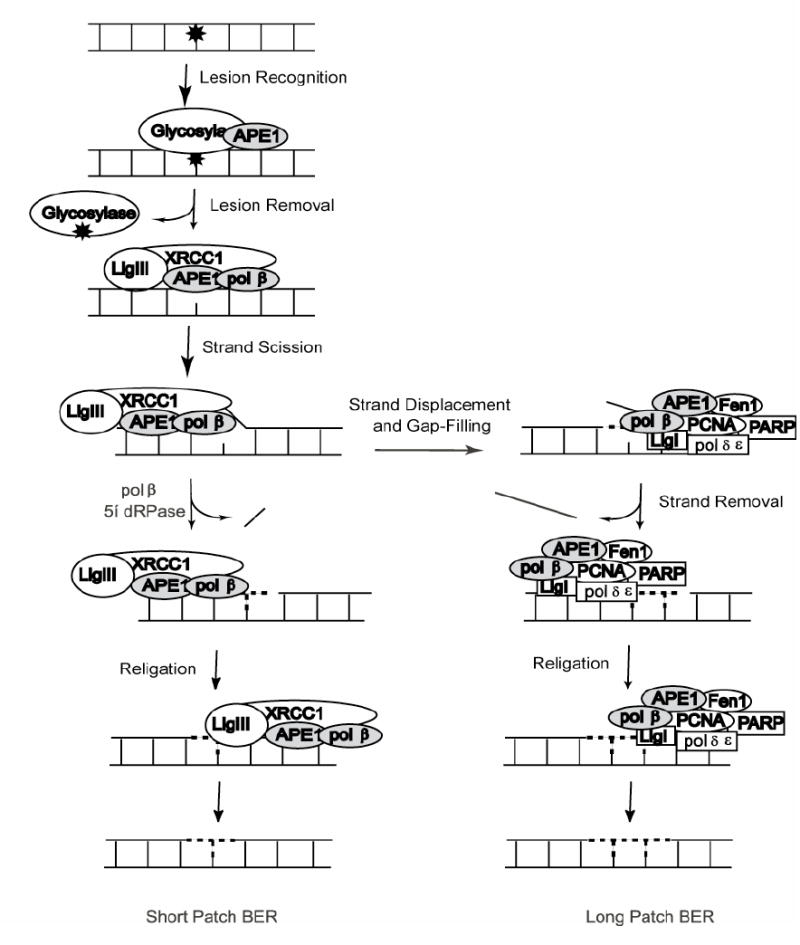
Short-patch pathway (left) depicts sub-pathway initiation by glycosylase activity followed by strand scission by APE1. Gap tailoring (5’dRP lyase) and nucleotide incorporation are accomplished by pol ß. The resulting nick is ligated by a complex of XRCC1 and LigIIIα to complete the pathway. Long-patch pathway (right) depicts a sub-pathway of BER responsible for repair under conditions of 5’lesions refractory to pol ß cleavage. In this case, BER complex formation shifts, nucleotide incorporation is conducted either by pol ß or is transferred to pol-δ or pol-•. The refractory 5’ moiety is removed as part of a flap of DNA by Fen1 and re-ligation is completed by LigI.
