Fig. 4. Effects of hypoxia, hypoxic exercise, and Ado infusion on vasoconstrictor responsiveness to endogenous norepinephrine release.
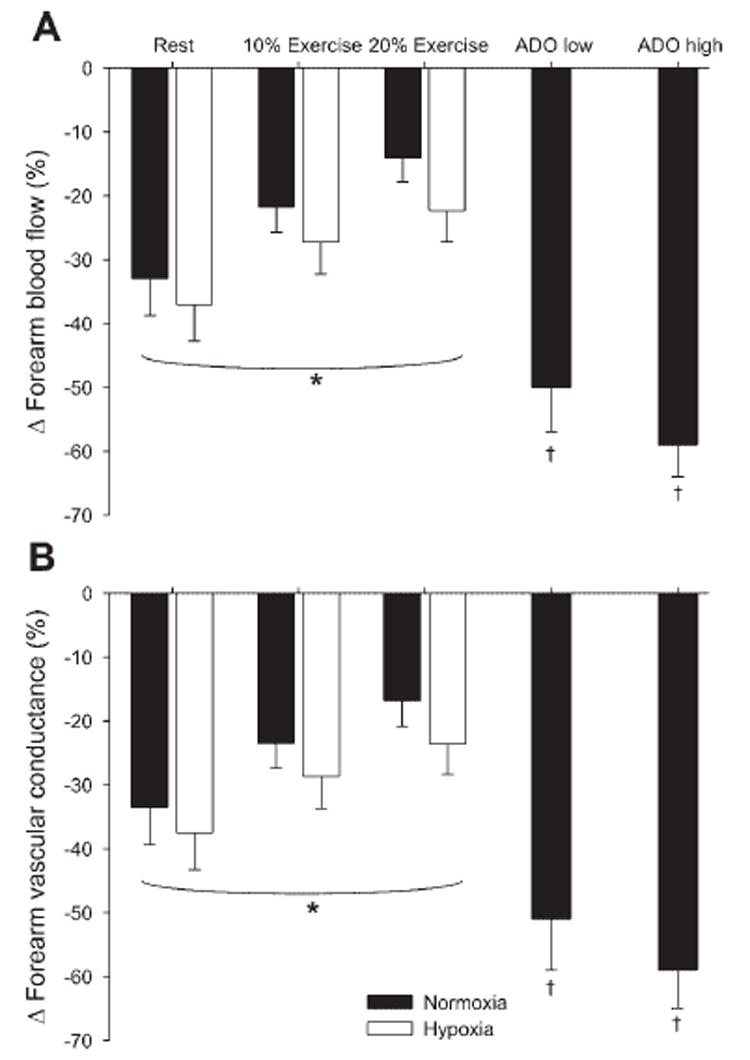
A: change (Δ) in forearm blood flow (%decrease) was blunted with increasing exercise intensity. However, Δ in forearm blood flow was similar between hypoxic exercise and normoxic exercise. The Δ in forearm blood flow during adenosine infusion was greater than both normoxic and hypoxic exercise. B: Δ in forearm vascular conductance (%decrease) decreased with increasing exercise intensity. However, Δ in forearm vascular conductance was similar between hypoxic exercise and normoxic exercise. The Δ in forearm vascular conductance during Ado infusion was greater than both normoxic and hypoxic exercise. Values are means ± SE. *Main effect of exercise, P < 0.01. †P < 0.01 vs. 10% and 20% exercise.
