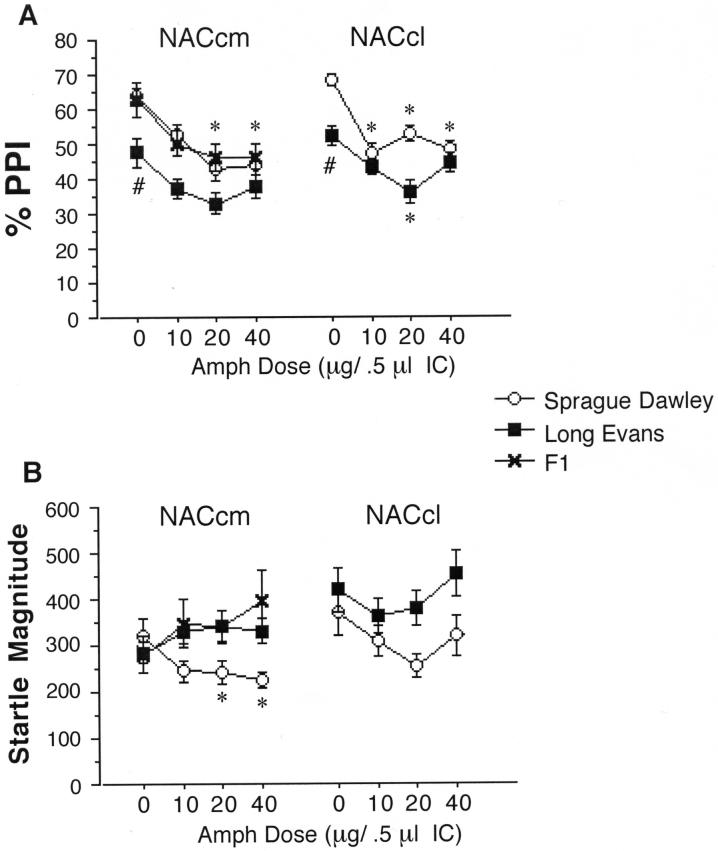
Figure 4.
PPI and startle magnitude after AMPH infusion in the NACcm in SD, LE and F1 rats, and into the NACcl in SD and LE rats. A. PPI is significantly reduced after AMPH infusion into the NACcm in SD rats (significant main effect of AMPH dose, p<0.005; * p<0.001 and p<0.002 for 20 and 40 μg doses, respectively). The main effect of AMPH on PPI also reached significance in F1 rats (p<0.03) but only approached significance in LE rats (p<0.06). In SD rats, PPI was also significantly reduced after AMPH infusion into the NACcl (main effect of AMPH dose, p<0.001; * p < 0.0005, p < 0.008 and p < 0.0005 for 10, 20 and 40 μg doses, respectively). After AMPH infusion into the NACcl n LE rats, the main effect of AMPH dose again marginally reached significance (p<0.051), with post-hoc comparisons revealing significantly reduced PPI after infusion of 20 μg AMPH (* p < 0.006). PPI after vehicle infusion into the NACcm or NACcl was also significantly lower in LE vs. SD rats (# p < 0.015, both sites). B. Startle magnitude is significantly reduced in SD rats after AMPH infusion into the NACcm (main effect of AMPH dose, p<0.03; * p < 0.001 and p < 0.002 for 20 and 40 μg doses, respectively).