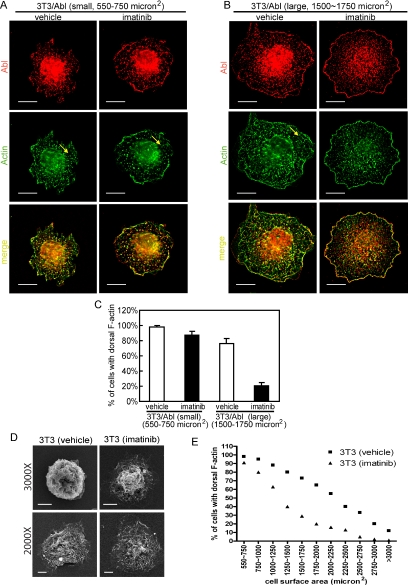
Figure 7.
Abl kinase prolongs dorsal ruffling during cell spreading. (A) and (B) 3T3/Abl cells treated with imatinib (5 μM) or vehicle (0.1% DMSO) were allowed to spread on FN (10 μg/ml)-coated coverslides, fixed at 20 or 40 min, stained with anti-Abl/Alexa 568–conjugated secondary antibody (red) and Alexa 488–conjugated phalloidin (green). Z-section images from the top of cells captured by deconvolution microscopy are shown. Yellow arrow points to F-actin–rich dorsal protrusions. (A) A representative image of a small cell (cell area from 550 to 750 μm2). Scale bars, 10 μm. (B) Representative images of a large cell (cell area from 1500 to 1750 μm2). Scale bars, 10 μm. (C) Quantitation of cells showing dorsal F-actin ruffles as described in Materials and Methods. (D) 3T3 cells treated with imatinib (5 μM) or vehicle (0.1% DMSO) were allowed to spread on FN-coated coverslides and fixed. Images were collected by scanning electronic microscopy (SEM) show dorsal ruffles in vehicle and imatinib treated cells. Scale bars, 5 μm. (E) 3T3 cells treated with imatinib or vehicle as in (D) were fixed at 20 or 40 min after plated on FN-coated coverslides. Individual cells were analyzed for size and dorsal F-actin protrusions as depicted in A and B. Cells were grouped into 11 categories based on size, and in each category, at least 50 cells were counted to determine the percentage of cells with dorsal F-actin ruffles.