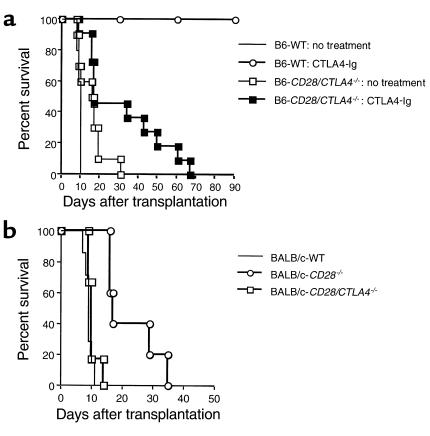
Figure 7.
Cardiac transplantation studies. (a) BALB/c (H-2d) hearts were transplanted to B6 (H-2b) wild-type or CD28/CTLA4–/– recipients with or without CTLA4-Ig treatment. Graft survival was slightly prolonged in CD28/CTLA4–/– recipients (MST 15.5 days, n = 10), but there was no statistical significance compared with wild-type recipients (MST 9.4 days, n = 5; P = NS). CTLA4-Ig treatment in wild-type recipients prolonged graft survival significantly (MST > 90 days, n = 3; P < 0.02) compared with nontreated wild-type recipients. CTLA4-Ig treatment also prolonged graft survival in CD28/CTLA4–/– recipients significantly (MST 31.5 days, n = 11; P < 0.05) compared with nontreated CD28/CTLA4–/– recipients; however, that prolongation was much less than in wild-type recipients (P < 0.005). (b) Vascularized B6 (H-2b) hearts were transplanted to BALB/c (H-2d) wild-type, CD28–/–, or CD28/CTLA4–/– recipients. The graft survival in CD28–/– recipients was prolonged (MST 22.6 days, n = 5) compared with both wild-type (MST 9.0 days, n = 7; P < 0.001) and CD28/CTLA4–/– recipients (MST 10.3 days, n = 6; P < 0.002). CD28/CTLA4–/– recipients rejected B6 heart grafts at the same tempo as wild-type recipients.