Fig 1.
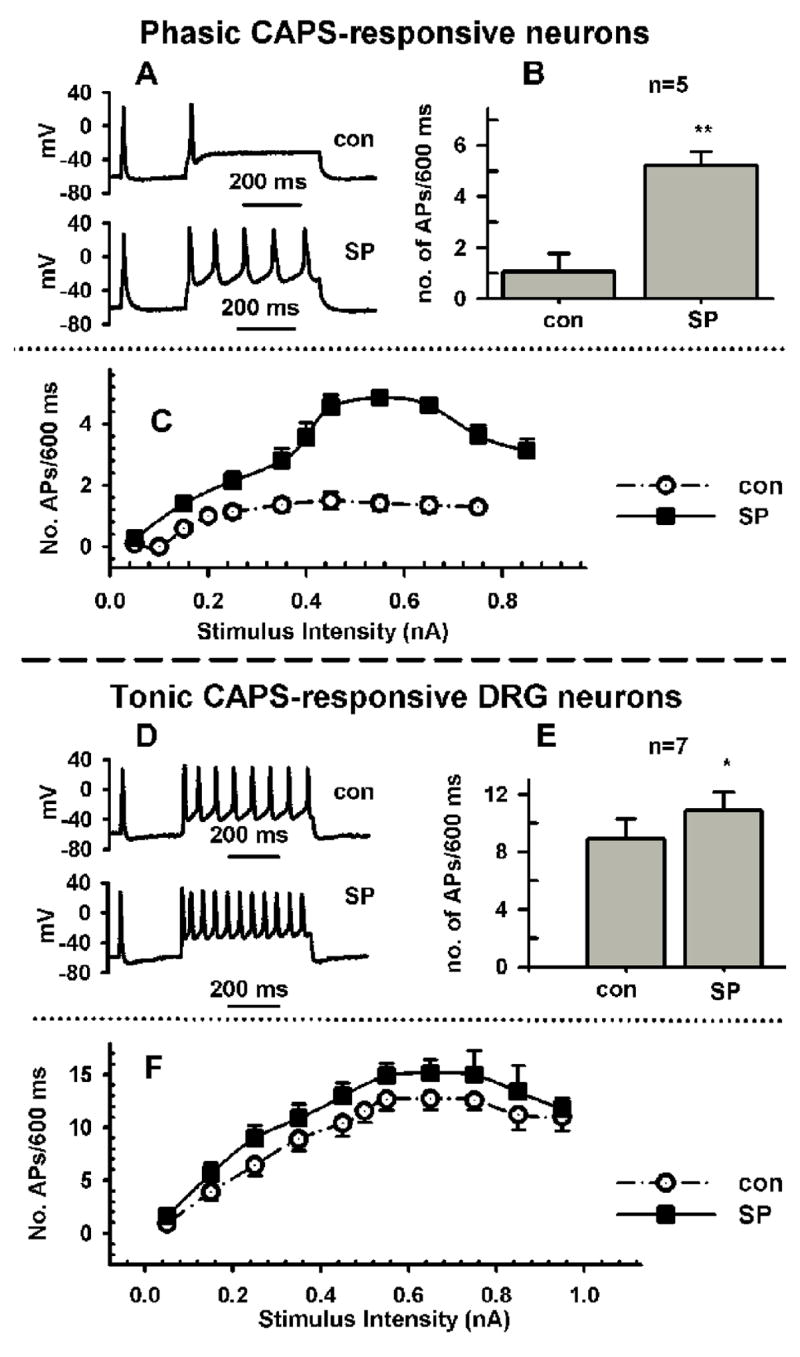
Effect of substance P (SP, A–F) in phasically firing neurons (A–C) and tonically firing (D–F) adult rat DRG neurons. A, SP (0.5 μM) increases firing in response to a current injection 600 ms long and 250 pA in intensity in a phasic neuron from 1 action potential (AP, control trace, con) to 5 AP. B, Average increase in APs in response to SP in 5 neurons. C, Dependence of firing on stimulus intensity for experiment in B, before (Control, empty circles) and after SP (0.5 μM, filled squares). D, SP (0.5 μM) increases firing in response to a current injection 600 ms long and 250 pA in intensity in a tonic firing neuron from 8 APs (control trace, con) to 11 APs. E, Average increase in APs in response to SP in 7 neurons. C, Dependence of firing on stimulus intensity for experiment in E, before (Control, empty circles) and after SP (0.5 μM, filled squares).
