Fig. 1.
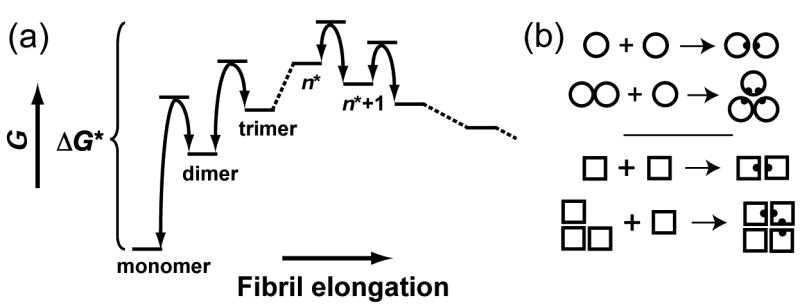
(a) Classical nucleation theory. Monomer addition is unfavorable until the critical nucleus is formed, which consists of n* peptides and is defined as the state with the highest free energy; addition of a monomer to an oligomer of n* or more peptides results in a lowering of the free energy. The rate of nuclei formation is proportional to e−ΔG*/kBT. (b) A cartoon illustrating the nature of cooperative association; two new interactions are formed when a monomer binds a dimer or trimer, whereas only one interaction is formed when two monomers associate.
