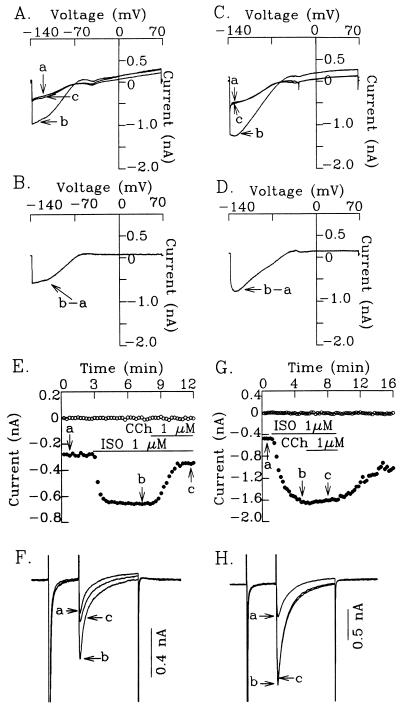
Figure 5.
Muscarinic cholinergic activation of IK-ACh and inhibition of isoproterenol (ISO)-stimulated ICa-L in cardiomyocytes from wild-type and Gαo−/− mice. (A–D) Normal activation of IK-ACh in atrial myocytes from wild-type (A and B) and Gαo−/− (C and D) mice. (A and C) Superimposed current traces showing control (a), effect of 1 μM carbamylcholine (CCh) (b), and effect of 1 μM atropine in the presence of CCh (c). (B and D) IK-ACh obtained by subtracting b. A ramp protocol (−140 to +70 mV) was applied to the cells at 0.09 V/sec. (E–H) Significant attenuation of CCh inhibition of ISO-stimulated ICa-L in murine ventricular myocytes from Gαo−/− mice. (E and G) Time course showing inhibition of ISO-stimulated ICa-L by CCh in murine ventricular cells from wild-type (E) and Gαo−/− mice (G). (F and H) Superimposed current traces showing control (a), effect of ISO (b), and effect of CCh in the presence of ISO (c). Current traces in F and H were taken from the time points marked in E and G, respectively. Holding potential was −80 mV. A prepulse to −40 mV was given to inactivate the fast inward sodium current (INa) and a further depolarizing pulse to 0 mV was applied to the cell to activate ICa-L. The horizontal lines in E and G indicate the time during which each test agent was applied. ○, Steady-state current level at −40 mV; and •, ICa-L.