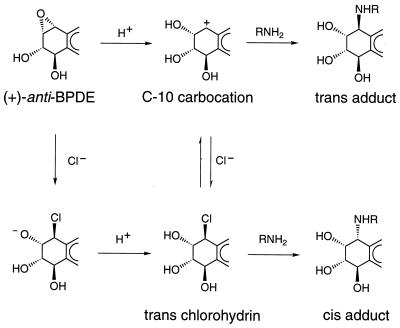
Figure 6.
The carbocation and chlorohydrin activation routes for the preferential formation of trans and cis adducts, respectively. The upper pathway depicts the acid-catalyzed formation of a C-10 carbocation intermediate, which generates primarily trans adducts with duplex DNA. Substantial amounts of cis products are also formed through this pathway by reaction with DNA monomers. The lower pathway depicts the mechanism we propose for the chloride ion-catalyzed formation of a cis adduct. The trans chlorohydrin would form exclusively cis adducts by an SN2 inversion of configuration. However, it can also lose chloride and generate trans products through a carbocation intermediate.