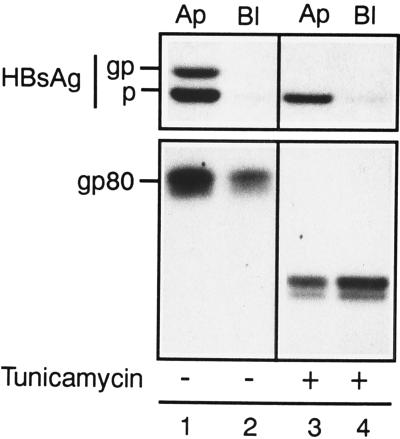
Figure 1.
Apical secretion of HBsAg is insensitive to tunicamycin inhibition of N-glycosylation, in contrast to endogenous gp80, in transfected MDCK cells. Permanent transfectants of MDCK cells forming impermeable monolayers in Transwell chambers were treated in the absence (lanes 1 and 2) or presence of tunicamycin (lanes 3 and 4), incubated 30 min with 100 mCi/ml [35]S-labeled methionine and cysteine, and chased for 6 h. Tunicamycin was added at low concentration (2 μg/ml) for 18–20 h and was increased to 12 μg/ml 2 h before the pulse-labeling period and maintained thereafter during the chase. Immunoprecipitates from the apical (Ap) and basolateral (Bl) media were resolved by SDS/PAGE, in either reducing or nonreducing conditions for HBsAg or gp80, respectively. The fluorograms of the gp80 secreted from cells treated with tunicamycin were exposed for longer periods to compensate for the inhibition of its secretion (16). Glycosylated (gp) and unglycosylated (p) forms of HBsAg are indicated.