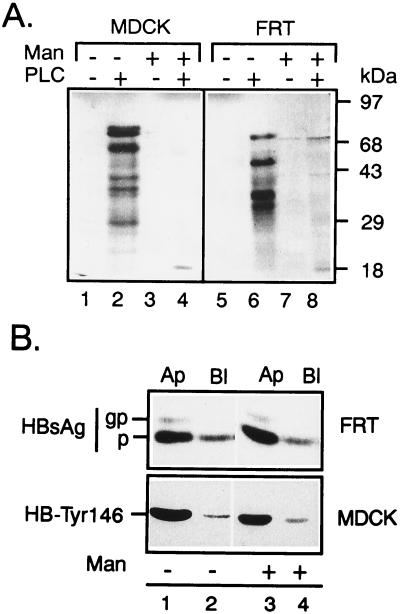
Figure 4.
Mannosamine treatment inhibits the biogenesis of GPI-anchored proteins in FRT and MDCK cells without affecting the apical secretion of HBsAg. (A) MDCK and FRT cells were preincubated for 6 h in glucose-free RPMI medium 1640 in the presence (+) or absence (−) of 10 mM mannosamine and then metabolically labeled for 18 h with 35S-labeled methionine and cysteine at 100 μCi/ml in glucose, methionine, and cysteine-free RPMI medium 1640, 1% FBS, and 20 mM Hepes, in the corresponding preincubation conditions. The cells were extracted with 1% Triton X-114 and subjected to temperature-induced phase separation, and the detergent phases were incubated with PI-PLC (6 units/ml) for 1 h at 37°C to provoke the partition shift of GPI-proteins into the aqueous phases (lanes 2, 4, 6, and 8). Metabolically labeled GPI-proteins become undetectable after mannosamine treatment (lanes 3, 4, 7, and 8). (B) The secretion of HBsAg from FRT cells and HB-Tyr146 from MDCK cells during mannosamine treatment (lanes 3 and 4) was indistinguishable from control conditions (lanes 1 and 2).