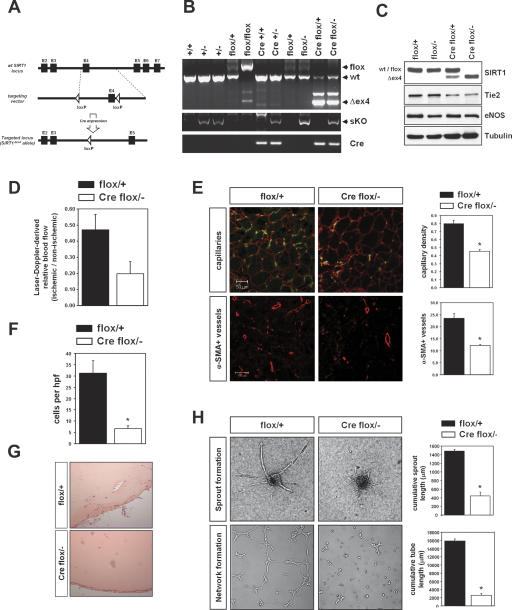
Figure 5.
Endothelial cell-specific deletion of SIRT1. (A) Strategy to generate a conditional SIRT1 allele by inserting loxP sites flanking exon 4 of the mouse SIRT1 genomic locus. The structure of the genomic locus, the targeting vector, and the targeted allele are shown. Endothelial-specific deletion was achieved by breeding to transgenic mice harboring a Tie2-Cre transgene. (B) Genotyping of the endothelial-specific SIRT1 mutant mice (Tie2Cretg;SIRT1flox/−). (Cre) Tie2Cretg; (flox) SIRT1flox allele; (+/−) SIRT1+/−. (C) Western blot analysis with a specific antibody against SIRT1 showed that the floxed SIRT1 allele was completely deleted in endothelial cells isolated from the endothelial-restricted SIRT1 mutant mice. Cell lysates were also subjected to Western blot analysis with antibodies targeting eNOS and Tie2 to show the endothelial characteristics of cells; tubulin served as loading control. (D) Mice of the respective genotypes were subjected to hindlimb ischemia, and perfusion was assessed 14 d after onset of ischemia using laser Doppler imaging. Quantitative results are presented. (E) Capillary (CD31, green; laminin, red) and α-smooth muscle actin staining (red) in sections of mice after hindlimb ischemia. A statistical summary of capillary density and the number of α-smooth muscle actin-positive vessels is shown. (F) Mice of the respective genotypes were subcutaneously injected with Matrigel matrix. After 7 d, Matrigel plugs were explanted and the hemoglobin content and invading cell number of the plug were quantified. (G) Histological analysis of H&E stainings from Matrigel plugs isolated from SIRT1flox/+ and Tie2Cretg;SIRT1flox/− mice. (H) Murine endothelial cells of SIRT1flox/+ and Tie2Cretg;SIRT1flox/− mice were isolated by vascular endothelial-cadherin immunopurification. Representative micrographs and statistical summary of the three-dimensional spheroid and Matrigel assay of in vitro angiogenesis with endothelial cells generated from these mice.